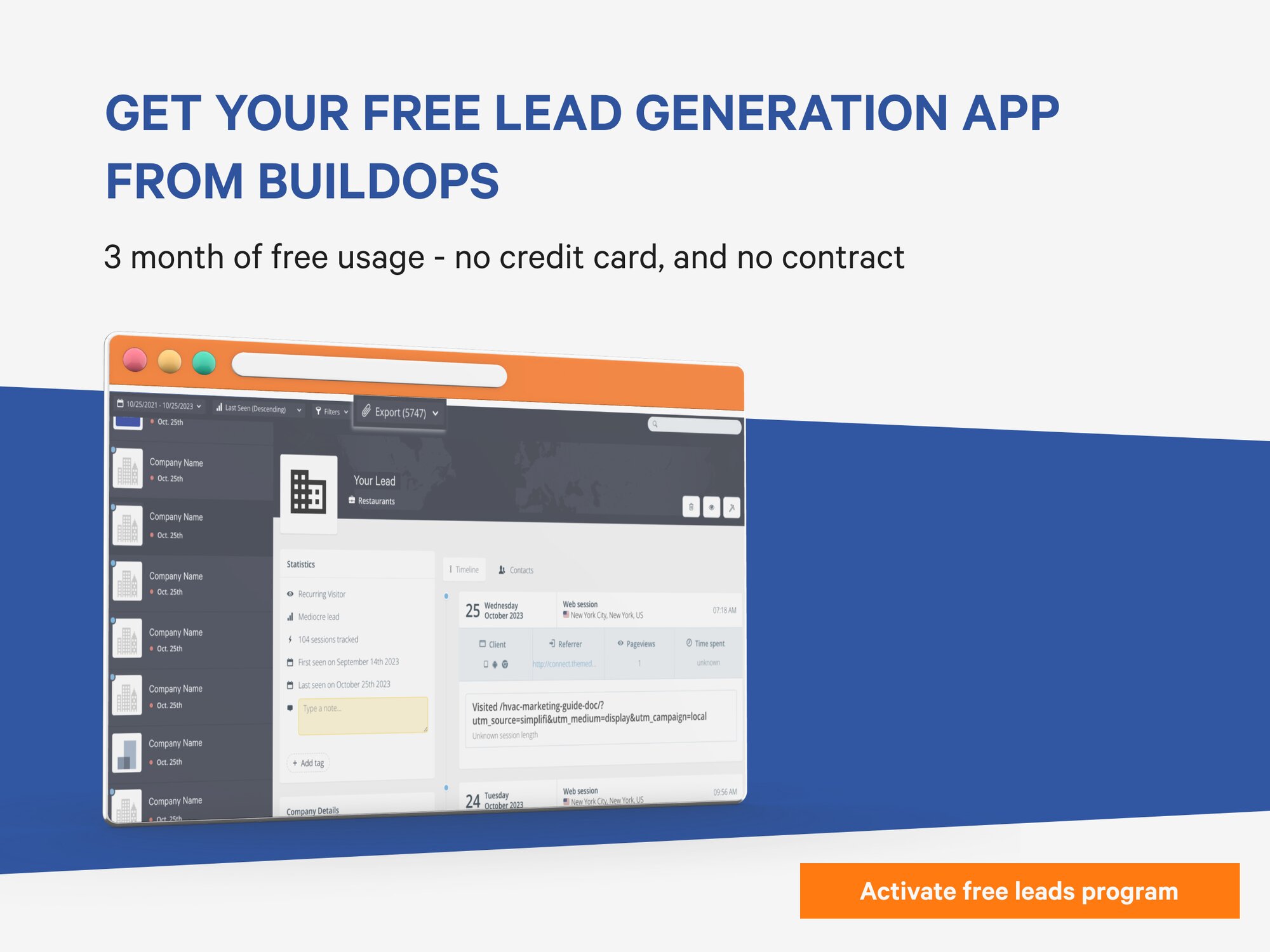
Vendor management systems are software solutions used to streamline and optimize the processes of contracting and managing vendors throughout their lifecycles. By doing this primary objective, organizations can more easily manage their supplier relationships, track and analyze vendor performance, and enforce consistently executed contracts and policies.
Vendor management systems typically offer a variety of features. They typically provide capabilities for organizations to gain insight into vendor data analytics, connect and collaborate with vendors, ensure contract compliance, track and manage more effectively, and protect sensitive data. Additionally, they are often mobile and cloud-based, enabling a higher degree of oversight and control over all supplier activities, resulting in improved decision-making, increased procurement efficiency, and lower operational costs.
These solutions can be used by organizations to streamline and automate the vendor management process by providing a comprehensive, secure, and user-friendly workflow system. This system makes it easier to capture and store critical information about vendor relationships and activities, as well as optimize the onboarding process of new vendors.
In addition, vendor management systems enable organizations to securely track all records across the lifecycle of the relationship, from initial planning stages to final payment. This helps organizations assess and monitor vendor performance, as well as ensure contract compliance and secured data protection.
Overall, vendor management systems are meant to automate and streamline the complex process of recruiting, contracting, and managing third-party vendors. They provide organizations with a secure and user-friendly system to monitor, assess and mitigate vendor-related risks, and create a more cost-effective and efficient management process.
Benefits of Using Vendor Management Systems
Vendor management systems provide a range of benefits to organizations and provide enhanced oversight. Benefits include improved decision-making, increased procurement efficiency, lower operational costs, secure storage of critical vendor data, efficient onboarding of new vendors, tracking of activities over the lifecycle of the vendor relationship, and improved monitoring and assessment of vendor performance. Additionally, they can also help organizations stay compliant with contracts and policies while protecting sensitive data. Ultimately, these systems are meant to create a more efficient and cost-effective vendor management process.
Common Features Offered by Vendor Management Systems
Vendor management systems typically provide a variety of features designed to streamline and automate the process of recruiting, contracting, and managing third-party vendors. Typical features include the ability to gain insight into vendor data analytics, connect and collaborate with vendors, ensure contract compliance, track and manage more effectively, and protect sensitive data. Additionally, they are often mobile and cloud-based, enabling secure onboarding of new vendors, tracking of activities over the lifecycle of the vendor relationship, and improved assessment of vendor performance. Ultimately, these systems are meant to create a more efficient and cost-effective vendor management process.
How to Select a Vendor Management System
Selecting a vendor management system (VMS) for an organization can often be quite a difficult task. Organizations should evaluate various factors such as cost, features, security levels, ease of implementation, and customer service before making their decision. Additionally, organizations should consider how the VMS will integrate with their existing systems, as well as what type of training and support will be necessary for its successful implementation. Furthermore, organizations should consider the scalability of the system, whether it can handle additional vendors as the organization grows. Ultimately, organizations should ensure the system meets their specific requirements, goals, and is fit for purpose.
Best Practices for Implementing a Vendor Management System
Implementing a successful vendor management system is key for organizations that wish to streamline the process of contracting and managing vendors. To ensure a smooth implementation, organizations should follow some best practices. These include evaluating factors such as cost, features, security levels, ease of implementation, and customer service prior to selecting a vendor management system. Furthermore, organizations should be sure their VMS of choice is compatible with existing systems and adequately scales with organization’s growth. Organizations should also ensure proper training is given to all involved parties in order to get the most out of the system. Finally, organizations should set up additional measures to ensure their VMS’s performance, security, and accuracy are consistently monitored. Following these best practices can help organizations make better decisions regarding their vendor management, as well as keep them compliant with policies and contracts.
Challenges of Vendor Management Systems
Using a vendor management system (VMS) is not without its challenges. Organizations must consider factors such as cost, features, security levels, ease of implementation, customer service, and scalability. Additionally, the system must be adequately trained and supported, with proper measures in place to monitor performance, security, and accuracy. Ultimately, a lack of proper implementation, training, and monitoring can result in inefficient processes that can lead to costly errors and breaches of compliance. Organizations should ensure they follow best practices for the selection and implementation of a VMS in order to successfully streamline vendor management.
Common Risks Involved with Vendor Management Systems
When selecting and implementing a vendor management system (VMS), there are several risks that organizations should be aware of. These risks include inadequate cost-benefit analysis, compatibility issues between the VMS and the organization’s existing systems, lack of training and support for users, scalability issues when the company grows, and security and privacy issues. All of these risks can lead to inefficient processes that can be costly and result in breaches of compliance, data loss, and reputational damage. To successfully manage their vendors and mitigate risks, organizations should select and implement their VMS properly and ensure proper training and monitoring of the system.
Advantages of Utilizing the System for Businesses
Utilizing a vendor management system enables businesses to streamline and optimize their processes when managing third-party vendors. This allows organizations to gain insight into vendor data analytics, connect and collaborate with vendors, ensure contract compliance, and securely track all vendor records. This system also makes it easier to onboard new vendors, track vendor performance, and protect sensitive data. Ultimately, using a vendor management system allows organizations to create a cost-effective and efficient process for managing vendors, while enabling improved decision-making and increased procurement efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Vendor management systems are essential tools for organizations to streamline and automate their vendor management process. They enable organizations to gain insight into vendor data analytics, connect and collaborate with vendors, ensure contract compliance, track and manage more effectively, and protect sensitive data. In addition, they help organizations assess and monitor vendor performance, onboard new vendors, and create a more cost-efficient and secure vendor management process. To get the most out of their vendor management system, organizations should select the right system that meets their specific requirements, goals, and fits their budget, while also ensuring proper implementation, training, and ongoing monitoring of the system.