Stop chasing payments. Start controlling your cash flow with invoicing built for the trades.

Invoicing slowing you down? You’re not alone. We analyzed thousands of invoices sent by commercial contractors across North America and found a simple truth:
Timing makes all the difference.
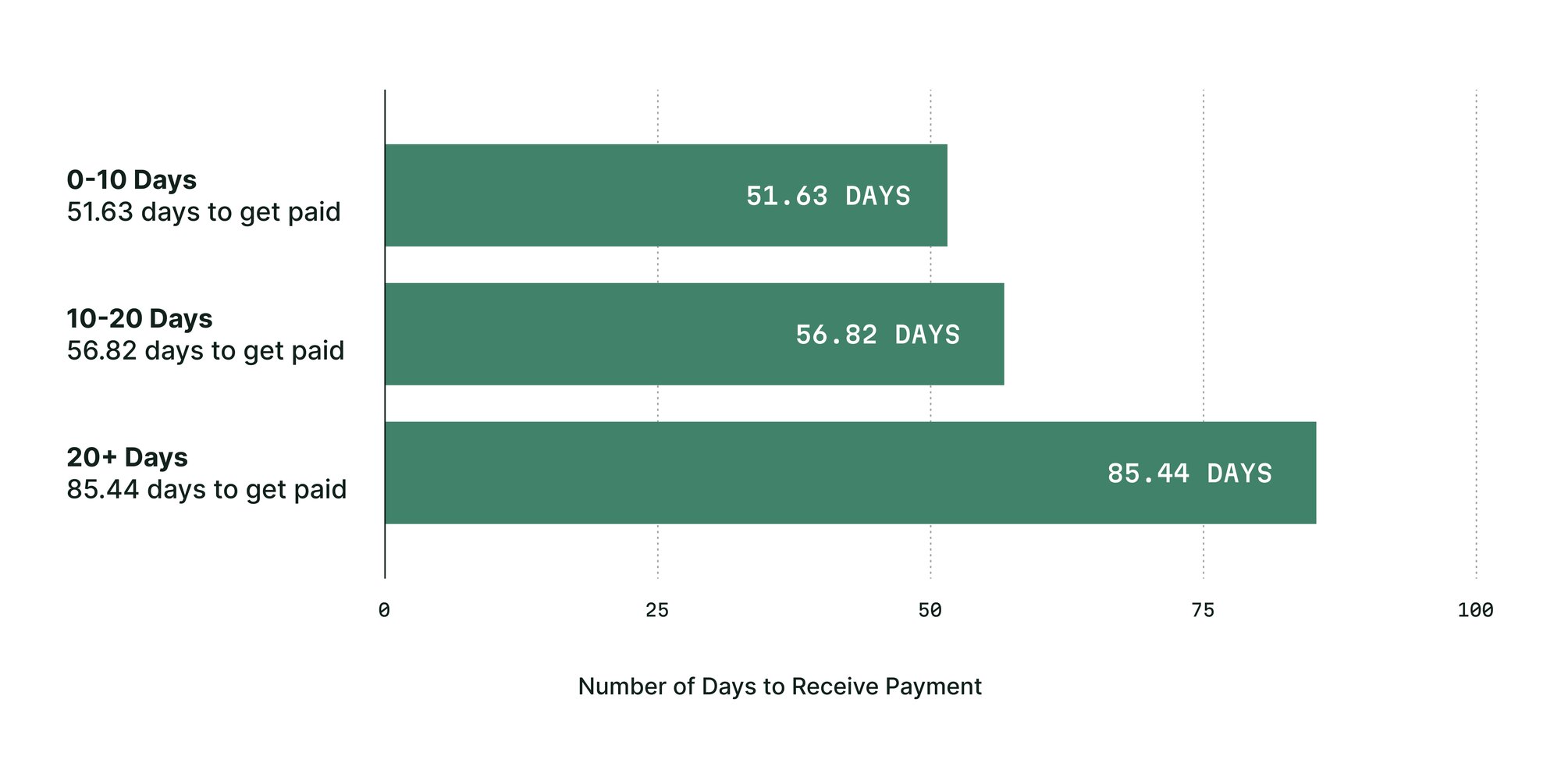
Get paid significantly faster.
Add 30+ days to your cash flow cycle.
Wait an average of 86 days to get paid.
Faster invoicing. Less waiting. More cash in hand.
Here’s how BuildOps makes it happen.



With BuildOps, it’s just part of the job no extra admin, no wasted time
Just invoices out, payments in.
Slowed down by invoicing delays? Grab the strategies top contractors use to speed up payments.
Cut the admin work. Speed up payments. Keep cash flowing
See how BuildOps puts invoicing on autopilot.
Invoicing software makes serious improvements to your invoicing process. Techs can generate the invoice, take payment, and send the finalized invoice back to the office in a matter of minutes.
The primary benefits are increased speed and error reduction. Paper invoices cause a number of headaches from deciphering illegible handwriting, lost paperwork, and taking longer to get paid.
BuildOps’ all-in-one platform enables you to simultaneously connect invoices to customer records and your accounting system. This results in a better experience for your customers, as well as higher efficiency and more informed decision-making for your business.
BuildOps integrates with many popular accounting solutions including QuickBooks, Sage, Vista, Spectrum, and more.









With BuildOps, commercial contractors have slashed billing time by 73%, grown revenue by 30%, and increased profits by 250%.
What can we do for you?