Executive Summary: Transactions & Payments Research Trends in the Construction Industry
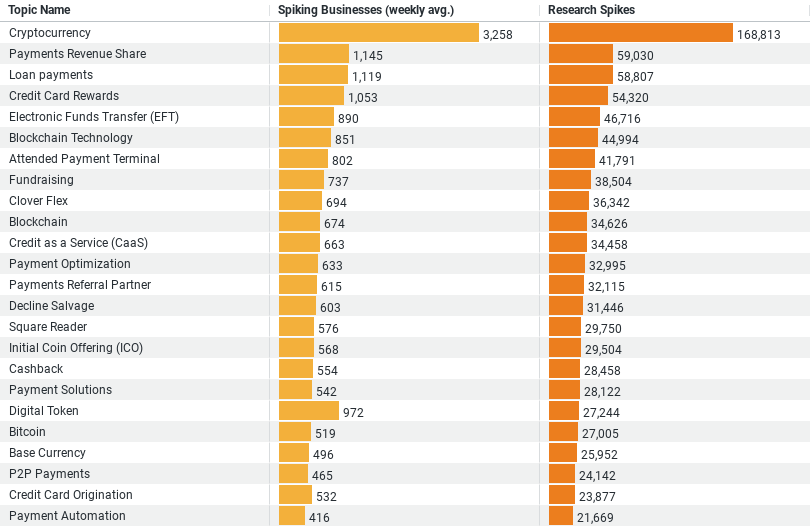
1. Cryptocurrency: Leads in interest with an average of 3,258 businesses spiking weekly beginning the first quarter of 2023. Ever since then, the topic has had a total of 168,813 research spikes, indicating a high level of interest and possibly exploration into utilizing cryptocurrencies for transactions and payments within the construction industry.
2. Payments Revenue Share: This topic, which involves sharing revenue through payment systems, sees an average of 1,145 businesses researching it weekly, with a total of 59,030 research spikes. This could reflect an interest in new revenue models through payment-sharing agreements.
3. Loan Payments: With 1,119 businesses on average researching this topic weekly and a total of 58,807 research spikes, there’s a significant interest in managing or facilitating loan payments. This could be related to financing construction projects or the purchase of equipment.
4. Credit Card Rewards: Shows an average weekly interest from 1,052 businesses and a total of 54,320 research spikes. The construction industry might be looking into leveraging credit card rewards as a means of reducing costs or benefiting from payment transactions.
5. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): An average of 890 businesses research this topic weekly, with a total of 46,716 research spikes. The interest here suggests a move towards more efficient, digital-first payment methods for transactions within the industry.
These insights indicate a strong interest in digital and innovative payment methods, such as cryptocurrency and electronic funds transfer, alongside traditional financial management topics like loan payments and revenue-sharing models. The construction industry appears to be exploring both cutting-edge and foundational financial practices to enhance its transactions and payment systems.
When analyzing company data across different sizes, the objective is often to identify trends, patterns, or behaviors that are specific to certain size categories. Companies are typically categorized into small, medium, and large based on various criteria such as revenue, number of employees, or market share. The analysis could focus on several key areas:
– Growth Trends: Larger companies might show steadier growth rates due to established markets and customer bases, whereas smaller companies could exhibit faster growth rates due to agility and innovation.
– Market Focus: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) might focus on niche markets or specialized services, while large companies may target broader markets or diversify their offerings.
– Investment in Innovation: This can vary significantly with company size. Larger companies often have more resources to invest in research and development, whereas smaller companies might prioritize immediate market needs and shorter development cycles.
– Risk Tolerance and Management Strategies: Larger companies usually have more structured risk management strategies, while smaller companies may take bolder risks to gain market share.
– Adoption of New Technologies: Small and medium-sized companies might be quicker in adopting new technologies to gain competitive advantages, whereas larger companies might face longer adoption cycles due to complexity and scale.
Why Trends Depend on Company Size
– Resource Availability: Larger companies typically have more resources, allowing them to invest in longer-term strategies, including market research, product development, and global expansion. In contrast, smaller companies might focus on short-term gains and rapid growth strategies.
– Market Agility: Smaller companies are often more agile, enabling them to respond quickly to market changes. This agility can be a significant advantage in fast-evolving sectors.
– Innovation and Risk: Smaller companies might be more willing to pursue innovative or risky ventures as a way to differentiate themselves in the market. In contrast, larger companies might pursue innovation within a more cautious and calculated framework.
– Customer Engagement: Smaller companies often have the ability to engage more closely with their customers, providing personalized services or products. This can lead to strong customer loyalty. Large companies, while having a broader reach, may need to work harder to achieve the same level of personalization.
Understanding these trends and their relationship with company size can provide valuable insights for businesses looking to strategize their growth, market positioning, or investment priorities. It can also help investors, analysts, and policymakers in making informed decisions or recommendations.