Executive Summary: Data Center Research Trends in the Construction Industry
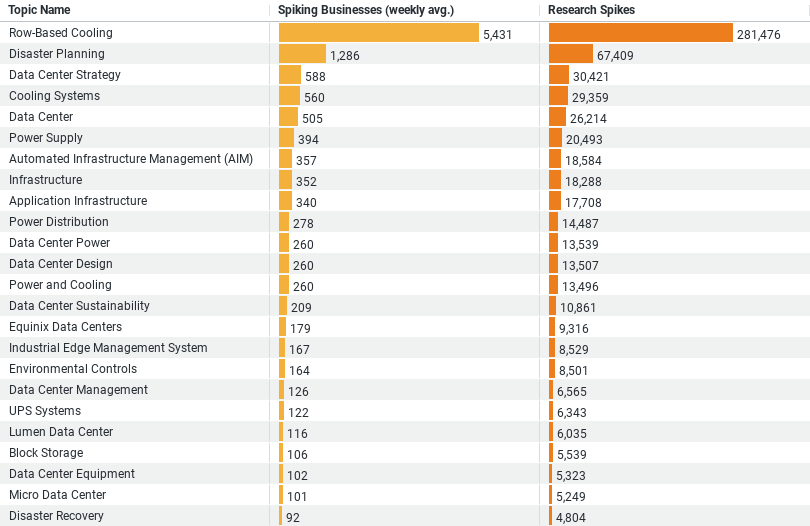
– Row-Based Cooling: Dominates the research with the highest engagement, showing a weekly average of approximately 5,431 businesses researching this topic, and a total of 281,476 research spikes.
– Disaster Planning: Also highly prioritized with about 1,286 businesses focusing on it weekly and accumulating 67,409 research spikes, underlining the importance of robust disaster management strategies.
– Data Center Strategy: Attracts around 588 businesses weekly with 30,421 research spikes, indicating a strategic focus on comprehensive planning and operation of data centers.
– Cooling Systems: Maintains high interest with 560 businesses exploring this weekly, leading to 29,359 research spikes, emphasizing the critical nature of cooling technologies in data center efficiency.
– Data Center: This broader topic sees about 505 businesses engaging each week, with a total of 26,214 research spikes, highlighting ongoing interest in various facets of data center operations.
Data Center Dynamics: Insights from the Construction Industry’s Research
The construction industry’s approach to research has always been keenly focused on addressing current needs while anticipating future challenges. A recent study delving into how the industry researches and develops its interests, particularly concerning Data Centers, provides a fascinating glimpse into the priorities and trends shaping the future of construction-related technology and infrastructure. This article highlights the most significant areas of research and interest, presenting a clear view of where the industry is headed.
Prioritizing Cooling Efficiencies: Row-Based and Cooling Systems
At the forefront of research is the topic of ‘Row-Based Cooling,’ which has seen the highest engagement among construction businesses, averaging about 5,431 companies exploring this area weekly. This technique involves placing cooling units directly in rows with servers, enhancing the cooling efficiency and reducing energy consumption. The significant number of research spikes, totaling 281,476, underscores its importance and points to an industry-wide push towards more sustainable and efficient data center designs. Similarly, the topic of ‘Cooling Systems’ garners substantial attention, with 560 businesses focusing on it weekly. This indicates a broader interest in innovative cooling technologies, crucial for maintaining optimal data center operating conditions and preventing hardware failures.
Disaster Planning: Ensuring Resilience and Continuity
Disaster Planning emerges as the second most popular research area, engaging about 1,286 businesses on a weekly basis with 67,409 research spikes. This highlights the construction industry’s focus on building data centers capable of withstanding various emergencies. The emphasis on disaster planning showcases the industry’s commitment to resilience, ensuring that data centers can continue to operate effectively in the face of disruptions, whether they are natural calamities or technological failures. The robust interest in this area signals a proactive approach to risk management, emphasizing the need for data centers that prioritize security and continuous operation.
Strategic Focus: Data Center Strategy and General Research
The study also sheds light on the strategic aspects of data center management through the lens of ‘Data Center Strategy,’ attracting about 588 businesses weekly. With 30,421 research spikes, it’s clear that there’s a keen interest in the overarching strategies that govern data center development and operation. This involves everything from the selection of locations to the integration of advanced technologies and the alignment with broader business objectives. Moreover, the general topic of ‘Data Center’ sees around 505 businesses engaging each week, accumulating 26,214 research spikes. This suggests an ongoing dedication to understanding the multifaceted nature of data centers, including their design, maintenance, and security.
Conclusion: The Path Forward in Data Center Research
The construction industry’s concentrated research on data center-related topics reflects a nuanced understanding of the critical role data centers play in today’s digital landscape. As the reliance on data processing and storage continues to escalate across various sectors, the need for data centers that are not only efficient but also resilient and strategically sound becomes more apparent. The insights from the current research trends indicate that the industry is well-aware of these demands and is actively pursuing innovations to meet them.
In conclusion, the construction industry’s research into data centers is driven by a clear recognition of the evolving requirements of technological infrastructures. By focusing on cooling efficiencies, disaster resilience, and strategic planning, the industry is not only addressing immediate operational concerns but is also paving the way for future advancements. This proactive and forward-thinking approach ensures that the construction of data centers continues to align with the rapid advancements in technology, making them more efficient, secure, and capable of supporting the increasingly digital world.
Company Sample Data: Trends by Company Size
Data Overview
– Company Size: Companies are categorized into five segments ranging from micro enterprises with 1 to 9 employees to medium-large enterprises with 500 to 999 employees.
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): This column indicates the average number of businesses within each size category that are showing a marked increase in activity or interest in a specific area weekly.
– Percent of Total: Represents the percentage of total spiking businesses accounted for by each company size category.
Trends by Company Size
1. Micro (1 – 9 Employees): Although these businesses are the smallest in size, they collectively contribute to a significant portion of the total, about 11.8%. This suggests a high level of agility and perhaps a greater ability or necessity to pivot or adapt to new opportunities or trends quickly.
2. Small (10 – 49 Employees): The highest level of weekly engagement comes from small companies, constituting approximately 32.4% of the total. This might reflect a robust operational capacity to engage with new technologies or market opportunities, combined with sufficient agility that larger companies may lack.
3. Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees): These companies account for roughly 28.6% of the activity, showing substantial engagement that might be driven by the resources to invest in research and development or new business strategies while still maintaining flexibility in operations.
4. Medium (200 – 499 Employees): Contributing to 11.6% of the total spikes, medium-sized companies might focus their efforts more strategically, possibly due to more substantial bureaucratic structures than smaller companies but significant adaptive capacity compared to larger enterprises.
5. Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees): These companies make up about 5.8% of the total, the lowest among the groups. This could indicate that while they have considerable resources, their size might constrain rapid changes or engagement with emerging trends as swiftly as smaller entities.
Implications of the Trends
The trend that emerges from the data is a clear inverse relationship between company size and the proportion of actively spiking businesses. Smaller companies tend to be more dynamic, possibly due to less red tape and a more pronounced need to stay competitive and innovative. In contrast, larger companies, despite their resources, may face challenges in rapidly adapting to market changes or in scaling new initiatives quickly.
This trend is significant because it highlights the potential advantages of size in terms of agility and innovation. It suggests that smaller firms might often be better positioned to capitalize on new opportunities quickly, a critical factor in fast-paced sectors such as technology, renewable energies, or even market strategies influenced by global trends.
In conclusion, understanding these dynamics can help stakeholders across industries to tailor their approaches to business development, partnerships, and market entry strategies according to company size and the inherent capabilities and challenges associated with each category.