Executive Summary: Researching Trends in the Construction Industry
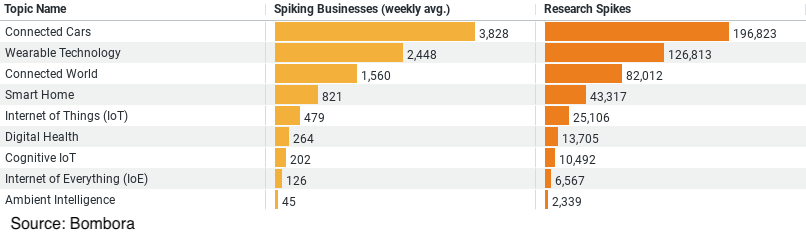
1. Connected Cars dominate the landscape with a weekly average of 3,828 businesses showing interest and a total of 196,823 research spikes, indicating a strong focus on vehicle technology and connectivity as a major area of interest and investment within the industry.
2. Wearable Technology holds significant attention, with 2,448 businesses engaged on average each week and 126,813 instances of research, reflecting the growing importance of personal tech in enhancing safety and productivity on construction sites.
3. Connected World, a broader category, sees interest from 1,560 businesses weekly and 82,012 research instances, suggesting an increasing investment in creating interconnected environments that can streamline operations and improve efficiency.
4. Smart Home and Internet of Things (IoT) show a targeted but growing interest with fewer businesses involved (821 and 479 weekly, respectively) but still substantial research activity (43,317 and 25,106 spikes, respectively). These areas are likely to expand as the industry explores more integrated and intelligent building solutions.
Construction Trends Unveiled: Researching Innovation in the Industry
The construction industry stands on the brink of a technological revolution, driven by rapid advancements in connectivity and digital solutions. As businesses and stakeholders actively seek out the latest innovations, research data reveals the most compelling trends, capturing the essence of where the industry is heading. This blog post delves into the key insights from recent data, outlining how construction professionals are aligning their research and interests with emerging trends.
Connected Cars: Leading the Charge
At the forefront of this shift is the growing interest in ‘Connected Cars’. Data indicates an impressive weekly average of 3,828 businesses researching this trend, with a staggering total of 196,823 research instances. The focus on connected cars suggests a strong inclination towards integrating advanced vehicle technology in construction. This trend not only emphasizes improving logistics and fleet management but also underscores a broader commitment to enhancing operational efficiency through technology.
Connected vehicles in construction promise to transform traditional practices, offering real-time data transfer, enhanced safety protocols, and more efficient use of resources. The adoption of these technologies can lead to significant cost savings and improved project timelines, which are critical factors in the competitive construction landscape.
Wearable Technology: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
Another significant trend is ‘Wearable Technology’, with 2,448 businesses exploring this area weekly, accumulating a total of 126,813 research interactions. Wearable tech in construction typically includes devices like smart helmets, vests, and watches that monitor health metrics and environmental conditions. These devices play a crucial role in ensuring worker safety, one of the industry’s most critical concerns, by providing real-time alerts and health monitoring to prevent accidents and manage hazards.
Moreover, wearable technology facilitates greater operational efficiency. By integrating data analytics, construction managers can optimize workflows and resource allocation based on the insights derived from wearable devices, driving productivity while safeguarding their workforce.
Connected World: Streamlining Operations
The ‘Connected World’ category, with 1,560 businesses engaging in research weekly and 82,012 total research instances, reflects a broader interest in creating interconnected environments. This trend includes the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices across construction sites, enabling seamless communication between machines and equipment. The connected world paradigm seeks to streamline operations and enhance monitoring and control systems, thereby reducing downtime and improving project management capabilities.
Smart Homes and IoT: The Future of Building
The interest in ‘Smart Homes’ and the broader ‘Internet of Things (IoT)’ highlights the industry’s forward-looking approach. Although these categories attract fewer businesses on a weekly basis (821 and 479, respectively), the research activity remains robust (43,317 and 25,106 research spikes, respectively). Smart home technology in construction extends beyond residential buildings, influencing commercial and industrial projects by integrating advanced automation and energy management solutions.
IoT technology’s role in construction extends to optimizing building operations, energy usage, and maintenance procedures, ensuring that buildings are not only more sustainable but also more economical to operate over their lifecycle.
Conclusion: Embracing a Tech-Driven Future
The construction industry’s research trends clearly indicate a shift towards embracing a tech-driven future. By investing in areas like connected cars, wearable technology, and smart, interconnected environments, the industry is setting the stage for profound changes in how construction projects are planned, executed, and managed.
As the industry continues to innovate, these trends offer a glimpse into the future of construction, where technology not only enhances efficiency and safety but also reshapes the very foundations of construction practices. With each research spike and business inquiry, the construction industry paves the way for a more connected, efficient, and safer future, proving that when it comes to construction, the future is truly built on innovation.
Company Sample Data Analysis
1. Company Size: Categorizes companies based on the number of employees, ranging from micro-sized (1-9 employees) to medium-large (500-999 employees).
2. Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): Indicates the average weekly number of businesses within each size category showing a spike in research or interest in a particular trend.
3. Percent of Total: Represents the proportion of each company size category contributing to the total number of businesses showing interest.
Here’s a breakdown of the insights and why these might be considered trends depending on various company sizes:
Micro Companies (1 – 9 Employees):
– Weekly Avg. Spikes: 909.6
– Percent of Total: 11.55%
– These companies show significant agility, often exploring new trends to find niche opportunities or innovative ways to compete with larger firms. Their smaller size allows for quick decision-making and adaptation, making them active in researching new trends.
Small Companies (10 – 49 Employees):
– Weekly Avg. Spikes: 2,443.2
– Percent of Total: 31.02%
– Small companies, which have more resources than micro companies, also demonstrate a strong interest in new trends. This segment likely has enough personnel and financial flexibility to invest in new technologies and strategies, aiming for growth and looking to leverage innovation for competitive advantage.
Medium-Small Companies (50 – 199 Employees):
– Weekly Avg. Spikes: 2,387.4
– Percent of Total: 30.31%
– Similar to small companies, medium-small businesses are actively engaging in new trends, possibly due to their capacity to pilot new technologies at a scale that can impact their operations significantly without the risk associated with larger organizational structures.
Medium Companies (200 – 499 Employees):
– Weekly Avg. Spikes: 957.6
– **Percent of Total: 12.16%
– Medium-sized companies, while still interested in new trends, show a lower relative activity compared to smaller companies. This may be due to more complex bureaucratic hurdles and slower adaptation processes, which can dampen their ability to rapidly integrate new trends.
Medium-Large Companies (500 – 999 Employees:
– Weekly Avg. Spikes: 436.7
– Percent of Total: 5.54%
– The lowest relative interest in trends among the categories, which could be attributed to the challenges of scaling innovations in larger environments. These companies might focus more on optimizing existing solutions rather than exploring new trends due to the complexities and risks involved in changing established systems.
Conclusion
The trend across various company sizes shows that smaller companies tend to be more engaged in researching new trends, likely due to their flexibility and the necessity to innovate for survival and growth. In contrast, as companies grow, the intensity of engaging with new trends decreases, possibly due to increased risk aversion and the complexities of implementing changes in larger operational scales. This pattern underscores the dynamic nature of business strategy and innovation, shaped profoundly by the size and structure of the organization.