Executive Summary: Staff Administration Research Trends in the Construction Industry
– Total Topics Analyzed: 5 different topics related to Staff Administration within the construction industry.
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): Measures the weekly average number of businesses that are actively researching each topic.
– Research Spikes: Total incidents of significant research activity recorded for each topic.
Key Data Points
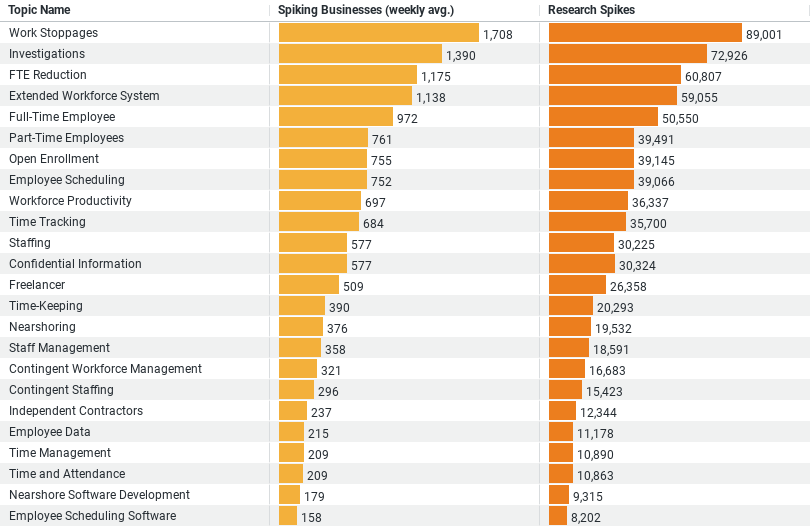
1. Most Researched Topic: “Work Stoppages” stands out as the most researched topic, with the highest weekly average of actively researching businesses (1708.48) and the highest total research spikes (89001).
2. Second Most Popular: “Investigations” follows with 1390.46 businesses researching on average per week and 72926 total research spikes.
3. Focus on Workforce Adjustment: Topics like “FTE Reduction” and “Extended Workforce System” show considerable interest, suggesting a focus on adjusting workforce strategies and enhancing systems for workforce management.
Analytical Insights
– Priority on Crisis Management: The data highlights a significant focus on crisis management within the industry, evidenced by high research numbers in topics like work stoppages and investigations.
– Economic and Operational Adjustments: The interest in topics related to staff reductions and system enhancements indicates ongoing adjustments to economic conditions and operational efficiencies within the sector.
Staff Administration Trends in the Construction Industry
The construction industry is continually evolving, facing unique challenges and opportunities that necessitate a deep understanding of various administrative functions. Recently, data on the research interests of businesses within this sector has shed light on critical trends in staff administration. This exploration reveals significant insights into the areas of crisis management, workforce adjustments, and systemic enhancements, reflecting the industry’s proactive approach to navigating a complex operational landscape.
Crisis Management Takes the Lead
Among the most researched topics, “Work Stoppages” has emerged as a primary concern, with an average of 1708.48 businesses investigating this issue each week. This topic alone has accumulated a total of 89,001 research spikes, indicating a heightened focus on managing unexpected disruptions effectively. Similarly, “Investigations” holds a spot as the second most researched area, with 1,390.46 businesses engaging weekly, resulting in 72,926 research spikes. The substantial interest in these areas underscores the construction industry’s urgency in managing crises and regulatory challenges efficiently. Such research is likely driven by the need to address potential legal and operational risks proactively, ensuring that projects proceed without significant interruptions.
Adjusting to Economic Pressures through Workforce Management
The topic of “FTE Reduction” also highlights an essential trend within the industry. An average of 1,174.81 businesses per week delves into this area, with total research spikes reaching 60,807. This trend points to the industry’s response to economic pressures by adjusting workforce sizes. Whether scaling up for large projects or scaling down in response to market downturns, businesses are keenly interested in strategies that allow them to remain agile and cost-effective.
Embracing Technological Advancements
Another noteworthy insight comes from the interest in the “Extended Workforce System.” With 1,137.56 businesses researching this weekly and a total of 59,055 research spikes, there is a clear indication that the construction industry is keen on enhancing workforce capabilities through technological solutions. This trend likely represents a shift towards digital transformation, where integrating advanced systems can lead to more efficient project management and labor allocation.
Maintaining a Steady Workforce
Research into “Full-Time Employee” issues, which sees 972.10 businesses engaged weekly and accounts for 50,550 research spikes, reflects ongoing concerns about maintaining a stable and reliable workforce. In a sector where project timelines and workforce demands can fluctuate drastically, having a core of dependable full-time staff is crucial for continuity and efficiency.
Strategic Implications for Industry Stakeholders
The data-driven insights into these topics are invaluable for various stakeholders within the construction industry. For business leaders, understanding these trends can aid in strategic planning and risk management. By aligning their operational strategies with these research interests, companies can better prepare for potential disruptions, optimize their workforce, and embrace technological advancements to stay competitive.
For policymakers and industry associations, these insights can guide the development of targeted support programs and regulations that address the specific needs and challenges of the construction sector. Ensuring that policies align with the primary concerns of businesses helps in fostering a more robust and resilient industry.
Conclusion
As the construction industry continues to navigate a rapidly changing economic and technological landscape, the focus on staff administration remains a cornerstone of strategic management. By investing in research across these pivotal areas, businesses not only prepare themselves for current challenges but also pave the way for future growth and stability.
The proactive approach in researching topics like work stoppages, workforce management, and technological integration highlights the industry’s commitment to excellence and its readiness to adapt to the ever-evolving market demands. This ongoing dedication to understanding and improving staff administration practices ensures that the construction industry remains at the forefront of operational and managerial innovation.
Company Sample Data
1. Company Size – Categorized into several groups based on the number of employees. These categories range from micro-sized businesses with 1-9 employees to large enterprises with over 1000 employees.
2. Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.) – The average number of businesses within each size category that show increased research or engagement activity weekly.
3. Percent of Total – The percentage that each company size category contributes to the total engagement across all categories.
Company Size Categories and Data:
1. Micro (1 – 9 Employees): Average of 798 businesses engaging weekly, representing about 9.48% of total engagement.
2. Small (10 – 49 Employees): Average of 2,275 businesses engaging weekly, making up 27.01% of the total.
3. Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees): Highest engagement with an average of 2,597 businesses weekly, accounting for 30.84% of the total.
4. Medium (200 – 499 Employees): Average of 1,243 businesses engaging weekly, representing 14.76% of the total.
5. Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees): Lower engagement with an average of 591 businesses, or 7.02% of the total.
Analysis and Trends:
– Scale of Business and Engagement: There is a clear trend where the engagement intensity peaks with medium-small businesses (50 – 199 employees) and then generally declines as company size increases. This could suggest that medium-small companies are at a developmental stage where they require more intensive research and engagement with operational topics to scale up effectively.
– Micro and Small Businesses: These businesses, while smaller in scale, still show significant engagement, likely due to the challenges they face in managing resources efficiently with limited manpower.
– Large Companies: The relatively lower percentage of total engagement among large companies could be attributed to established systems and processes that require less frequent adjustment, or it may reflect a greater reliance on internal resources rather than external research for operational improvements.
Conclusion
The data suggests a significant variation in how companies of different sizes prioritize and engage with key operational topics. Medium-small businesses appear most active, possibly indicating a crucial phase of growth and operational scaling. In contrast, larger enterprises show less proportional engagement, which could reflect stability or different approaches to innovation and problem-solving. Understanding these dynamics can help service providers and policymakers tailor their offerings and support to meet the unique needs of businesses at different growth stages.