Executive Summary: Security Technology Research Trends in the Construction Industry
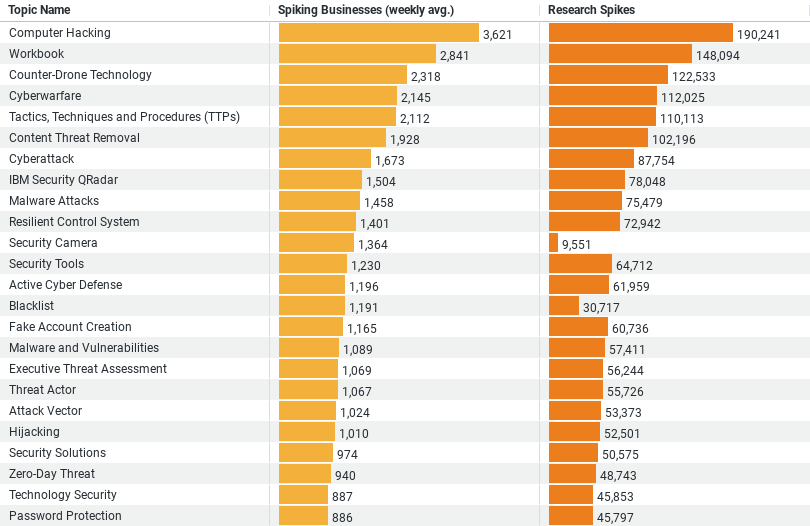
1. Computer Hacking is the leading topic of interest, with a weekly average of 3,620.57 spiking businesses and a total of 190,241 research spikes. This indicates a high level of concern and interest in preventing hacking incidents.
2. Workbook, potentially related to software or systems managing security data or processes, follows with 2,840.65 spiking businesses weekly and 148,094 total research spikes, suggesting significant interest in managing and documenting security practices.
3. Counter-Drone Technology ranks third, showing considerable interest from 2,318.15 spiking businesses weekly and a total of 122,533 research spikes. This reflects the growing concern over unauthorized drone activities around sensitive construction areas.
4. Cyberwarfare is another critical area of focus, with 2,144.87 spiking businesses weekly and 112,025 total research spikes, indicating the industry’s awareness and preparation against cyber threats that could impact construction operations.
5. Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs), with 2,112.37 spiking businesses weekly and 110,113 total research spikes, highlights the emphasis on strategic approaches to security, encompassing various tactics, techniques, and procedures employed to enhance security measures.
These trends reveal a robust and varied interest in security technologies within the construction industry, focusing not just on cyber threats but also on physical and operational security challenges. The data underscores the importance placed on safeguarding against hacking, managing security operations efficiently, addressing the emerging threat of drones, preparing for cyber warfare, and adopting comprehensive security strategies.
The Leading Concern: Computer Hacking
At the forefront of security concerns in the construction industry is the threat posed by computer hacking. Data reveals a staggering weekly average of 3,620.57 businesses showing a spike in research related to hacking, with a total of 190,241 research spikes observed. This highlights the acute awareness within the industry of the potential damages hacking can inflict, not just in terms of financial loss but also in the possible compromise of sensitive project data and operational integrity. The emphasis on combating computer hacking signifies a prioritized investment in cybersecurity measures, aiming to fortify the industry against digital intrusions.
Operational Security: Workbook and Counter-Drone Technology
Following closely behind the concern for hacking is the interest in operational security measures, as seen in the research spikes for “Workbook” and “Counter-Drone Technology.” The term “Workbook” likely refers to the comprehensive management and documentation tools used in outlining security practices and procedures. With 2,840.65 weekly spiking businesses and 148,094 total research spikes, it’s clear that there is a significant focus on ensuring that security operations are meticulously planned and recorded.
Moreover, the construction industry is also paying close attention to the emerging threat of drones, with “Counter-Drone Technology” research showing 2,318.15 weekly spiking businesses and a total of 122,533 research spikes. This reflects the growing concern over unauthorized drone flights that could pose risks to site security and privacy, highlighting the need for technology solutions that can detect and neutralize potential drone-based threats.
Cyberwarfare and Strategic Security Planning
Another area of concern that the data points to is cyberwarfare, with 2,144.87 weekly spiking businesses and 112,025 total research spikes. This indicates an understanding within the construction industry of the broader cyber threat landscape, where threats may not only come from individual hackers but also organized cybercriminal entities or even state-sponsored attacks. The focus on cyberwarfare suggests an acknowledgment of the need for robust, comprehensive cybersecurity strategies that can protect against a wide range of digital threats.
Lastly, the interest in “Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)”—with 2,112.37 weekly spiking businesses and 110,113 total research spikes—emphasizes the strategic approach the construction industry is taking towards security. This involves not just the adoption of specific technologies or measures but a holistic view of security that incorporates a variety of tactics and procedures designed to enhance overall resilience against threats.
Conclusion
The construction industry’s focused research into security technology reveals a proactive and multifaceted approach to addressing both cyber and physical security challenges. From the high level of concern over computer hacking to the strategic interest in operational security measures and emerging threats like drones, it’s evident that the industry is taking comprehensive steps to safeguard its operations. This data-driven insight underscores the importance of continued investment in security technology and strategic planning to navigate the complexities of the modern threat landscape effectively.
As the construction industry continues to evolve and integrate more digital tools and platforms into its operations, the focus on security technology will undoubtedly remain a top priority. By staying informed on the latest trends and insights, businesses within the sector can better prepare themselves to tackle the security challenges of tomorrow, ensuring the integrity, safety, and success of their projects in the digital age.
Company Sample Data
Micro (1 – 9 Employees)
Micro-sized companies, despite their small scale, show a considerable interest in security technology, with an average of 2,677.23 spiking businesses weekly. This represents 12.76% of the total, suggesting that even the smallest enterprises recognize the importance of cybersecurity in safeguarding their operations. The high level of engagement could be driven by the relatively larger impact that security breaches can have on smaller businesses.
Small (10 – 49 Employees)
Small companies demonstrate the highest weekly average of spiking businesses at 6,939.85, accounting for 33.08% of the total interest. This significant engagement indicates that as companies grow, so does their awareness and investment in security technology. Small businesses likely face more complex security challenges than micro enterprises, driving a greater need for comprehensive security solutions.
Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees)
Medium-small companies show a slightly lower weekly average than small businesses, with 6,474.92 spiking businesses, yet they contribute a substantial 30.86% to the total. This slight decrease might reflect a transition phase where businesses start to implement more robust security frameworks and practices, potentially leading to a temporary stabilization in the spike of interest as they assess and integrate these technologies.
Medium (200 – 499 Employees)
Medium-sized companies, with an average of 2,422.48 spiking businesses weekly, contribute 11.55% to the total. The drop in interest compared to smaller companies might be attributed to these businesses having established security measures in place, leading to a more consistent and less spiked interest in new technologies.
Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees)
Medium-large enterprises show the lowest weekly average of 1,042.08 spiking businesses, making up 4.97% of the total interest. This trend could suggest that as companies reach a certain size, they have a more established security technology infrastructure, leading to less frequent spikes in researching new security technologies. Alternatively, it could reflect a shift towards in-house development or bespoke solutions that are not captured by the data on spiking interest.
Trend Analysis and Implications
The data reveals a clear trend: smaller companies (from micro to small and medium-small) exhibit a higher and more dynamic interest in security technology, likely driven by the growing complexity of their operations and the increasing cyber threats they face. As companies grow, the trend shifts, with larger companies (medium and medium-large) showing a steadier interest, possibly due to having more established security measures or a focus on customized solutions.
Additionally, this pattern underscores the critical role of security technology across all company sizes, with varying degrees of engagement reflecting different stages of security infrastructure maturity and strategy adaptation. For smaller companies, the focus is likely on establishing robust security foundations to protect against immediate threats. In contrast, larger companies may prioritize refining and enhancing existing systems to counter evolving security challenges.
Lastly, understanding these trends is essential for security technology providers, as it enables them to tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs and behaviors of companies at different growth stages. For companies themselves, recognizing where they fall in this spectrum can help them assess their security technology strategies and ensure they are adequately prepared to face current and future threats.