Executive Summary: *Technology Database Research Trends in the Construction Industry
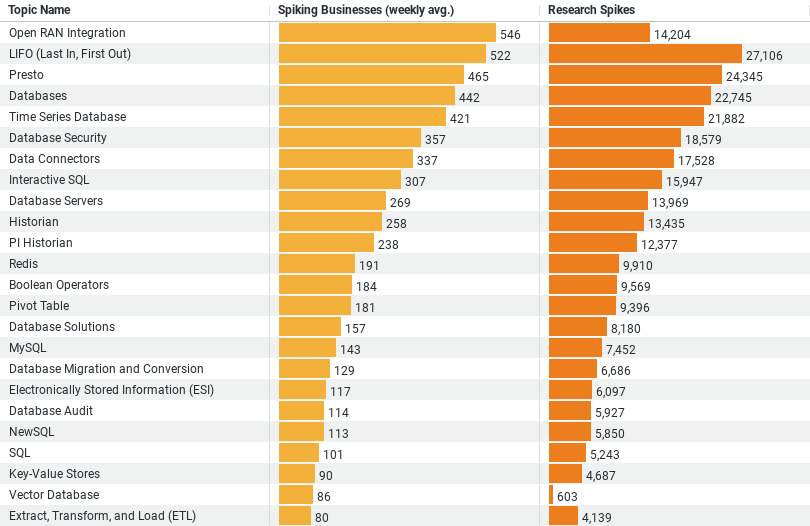
– Highest Interest Area: Open RAN Integration leads with an average of 546 spiking businesses weekly, signifying a robust interest in integrating open radio access networks, likely driven by the benefits of interoperability and network efficiency.
– Resource Management: LIFO (Last In, First Out) stands out with 522 spiking businesses weekly, highlighting the construction sector’s focus on optimizing inventory and material management strategies.
– Big Data Analytics: Interest in Presto, evident from 465 spiking businesses weekly, illustrates the sector’s inclination towards leveraging big data analytics for insightful decision-making and operational enhancements.
– General Technology Adoption: The general category of Databases, with 442 spiking businesses weekly, and Time Series Database, with 421 weekly, reflect a broad interest in database management systems. This shows an acknowledgment of the critical role of data management in project planning, execution, and progress tracking.
– Research Spikes: The topics show significant research spikes, with Open RAN Integration at 14,204 and LIFO at 27,106, indicating acute research interests and potential shifts towards these areas.
This summary encapsulates the construction industry’s growing engagement with technology, focusing on communication networks, resource management, and data analytics to drive efficiency and effectiveness in operations.
Top of the Tech Stack: Open RAN Integration
Leading the charge is the industry’s keen interest in Open RAN Integration, with an average of 546 spiking businesses weekly. This trend underscores a significant shift towards open radio access networks, highlighting the construction sector’s move to adopt open standards for improved interoperability, flexibility, and network efficiency. The embrace of Open RAN Integration reflects a broader industry ambition to leverage cutting-edge communication technologies, ensuring seamless data exchange and collaboration across diverse project environments.
Streamlining Operations: LIFO Strategy
Another noteworthy trend is the industry’s focus on the Last In, First Out (LIFO) inventory management strategy, drawing attention with 522 spiking businesses weekly. This approach, traditionally associated with accounting and inventory management, is now being reinterpreted in the context of construction to optimize material handling and resource allocation. The LIFO method’s adoption is indicative of the industry’s proactive efforts to mitigate waste, enhance supply chain dynamics, and ensure project materials are utilized efficiently and cost-effectively.
Harnessing Big Data: The Presto Revelation
The construction industry’s exploration into big data analytics is epitomized by its interest in Presto, a distributed SQL query engine. With approximately 465 spiking businesses weekly, Presto’s prominence highlights the sector’s inclination towards harnessing big data for informed decision-making. The ability to efficiently query vast datasets across multiple sources enables construction firms to derive actionable insights, from project feasibility studies to operational optimizations, heralding a new era of data-driven construction management.
Foundational Focus: Database Technologies
A general interest in database technologies, with 442 spiking businesses weekly, and a specific focus on Time Series Databases, with 421 weekly, reveal a foundational emphasis on robust data management solutions. These technologies are critical for organizing, storing, and analyzing project-related data, from scheduling and progress tracking to resource allocation. The construction industry’s engagement with these databases reflects a strategic recognition of the importance of scalable, reliable data storage and analysis tools in managing the complexities of modern construction projects.
Insightful Research Spikes
The data also highlights significant research spikes across these topics, with Open RAN Integration and LIFO strategies leading the way. These spikes are not merely numerical; they represent a collective industry effort to deepen understanding, evaluate applications, and implement technologies that promise to revolutionize construction practices.
Conclusion
The construction industry’s focused research into technology databases signals a transformative period. By embracing Open RAN Integration, LIFO strategies, Presto, and other database technologies, the sector is laying the digital groundwork for future projects. This pivot towards technology is not just about adopting new tools; it’s about reimagining construction processes through the lens of data, efficiency, and innovation.
As the industry continues to navigate its digital transformation, these insights into technology database research provide a roadmap for other sectors. The construction industry’s journey underscores the universal relevance of digital adaptation, marking a blueprint for integrating technology to tackle traditional challenges, enhance operational efficiency, and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly data-driven world.
Company Sample Data
– Company Size Categories: The dataset categorizes companies into five groups based on the number of employees: Micro (1 – 9 Employees), Small (10 – 49 Employees), Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees), Medium (200 – 499 Employees), and Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees).
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): This column quantifies the average weekly interest (spike in research or engagement) that companies within each size category are showing towards specific technologies or trends.
– Percent of Total: Reflects the proportion of total spiking businesses that each company size category represents.
Insights and Trends
– Dominant Interest from Medium-Small Companies: With 830.94 average weekly spiking businesses, medium-small companies (50 – 199 Employees) demonstrate the highest engagement level, accounting for 25.02% of the total. This suggests a significant inclination towards adopting or researching new technologies among companies within this size bracket, likely due to their agility and sufficient resources to invest in innovation.
– Active Small Businesses: Small businesses (10 – 49 Employees) also show considerable activity with 720.87 weekly spikes, making up 21.71% of the total. This category’s active interest indicates a keen pursuit of technological advancements to compete effectively and optimize operations.
– Micro and Medium-Large Companies: While micro (1 – 9 Employees) and medium-large (500 – 999 Employees) companies have lower weekly spikes, with 266.40 and 323.58 respectively, their engagement levels underscore a diverse interest in technology across all company sizes. Micro enterprises show a proactive stance towards exploring new trends, possibly to leverage technology for growth and scalability. In contrast, medium-large companies may focus on specific technologies that align with their strategic goals, reflecting in their 9.74% contribution to the total spikes.
– Medium Companies’ Engagement: Medium-sized companies (200 – 499 Employees) with 501.65 weekly spikes and 15.11% of the total indicate a balanced but significant interest in technology. This suggests that these companies are actively exploring technological solutions to enhance their operations, albeit with a focused approach perhaps due to the complexities of scaling and managing larger teams.
Why This Is a Trend
The dataset illustrates a broad and active engagement with technology across companies of various sizes, highlighting a general trend towards digital transformation and technological adoption. This interest is driven by several factors:
– Competitive Advantage: Companies strive for innovation to stay competitive. Technology can streamline operations, reduce costs, and open new revenue streams.
– Operational Efficiency: There’s a growing recognition of how technology can improve efficiency, from automating routine tasks to optimizing supply chains.
– Scalability and Growth: Especially for micro and small businesses, technology offers tools for scaling operations and reaching wider markets without proportionately increasing overheads.
– Customer Expectations: Across sectors, customers expect more personalized and efficient services, pushing companies to adopt technology to meet these demands.
This trend reflects the evolving business landscape where technology plays a crucial role in enabling companies of all sizes to achieve their objectives, adapt to market changes, and foster innovation for sustainable growth.