Executive Summary: Privacy Research Trends in the Construction Industry
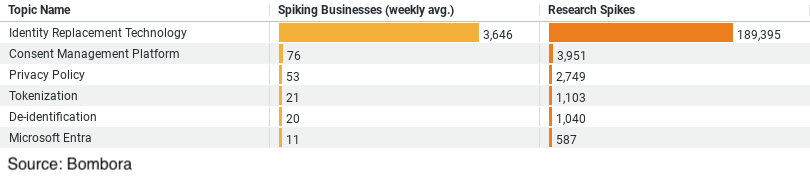
– Identity Replacement Technology leads with the highest interest, both in terms of average weekly engagement from businesses (approximately 3,645.56) and total research spikes (189,395), indicating a major focus on innovative identity management solutions.
– Consent Management Platform and Privacy Policy follow, with significant interest likely due to regulatory demands, showing average weekly engagements of about 76 and 53 businesses respectively, and research spikes of 3,951 and 2,749.
– Tokenization and De-identification are also notable but with lower engagement levels (average weekly engagements of about 21 and 20 businesses respectively), with research spikes reflecting focused but less extensive interest (1,103 and 1,040 respectively).
Privacy Innovations in Construction: Trends and Insights
The construction industry, often seen as traditional in its methods and approaches, is increasingly turning its focus towards modern challenges, particularly in the realm of data privacy and security. As businesses become more digital, the importance of managing personal and confidential information responsibly cannot be overstated. Our recent analysis reveals a significant uptick in research and development within the construction sector related to privacy, showcasing a proactive approach towards embracing technology to safeguard data.
Identity Replacement Technology: Leading the Charge
The most striking insight from our data is the substantial interest in Identity Replacement Technology. With an average weekly engagement from businesses at approximately 3,645 and research spikes totaling 189,395, this technology stands out as the frontrunner. The construction industry’s keen interest in this area suggests a shift towards more secure and innovative ways of managing identities on construction sites and within project management systems. This technology can replace traditional methods of identification, potentially reducing the risk of data breaches and enhancing privacy by obfuscating personal details in a way that they remain useful without being exploitable.
Privacy Policies: Essential Frameworks
Our data also highlights a solid focus on the development and refinement of Privacy Policies, with an average of 53 businesses per week delving into this topic, accumulating a total of 2,749 research spikes. Privacy policies are fundamental for transparency, outlining how data is collected, used, and protected. In the construction industry, where projects often involve numerous contractors and subcontractors, having a robust privacy policy ensures that all parties understand their rights and obligations, thereby protecting both the business and its clients.
Tokenization and De-identification: Enhancing Data Security
Tokenization and De-identification are techniques that have piqued the interest of the construction sector, albeit to a lesser extent compared to the technologies discussed earlier. These methods focus on protecting sensitive information by transforming it into a format that cannot be easily associated with an identifiable person without additional information. Tokenization, which secures sensitive data by replacing it with unique identification symbols, and De-identification, which removes identifying details from data sets, are critical for mitigating risks associated with data breaches. With average weekly engagements of 21 and 20 businesses respectively, and research spikes of 1,103 and 1,040, these technologies represent a growing interest in securing project data and client information in a comprehensive manner.
Conclusion
The construction industry’s increasing research into privacy-related technologies and strategies reflects a broader trend of digital transformation within the sector. By investing in advanced technologies such as Identity Replacement Technology, Consent Management Platforms, and robust privacy frameworks, the industry is not only enhancing its operational efficiency but also fortifying its defenses against data breaches and compliance risks. As construction companies continue to navigate the complexities of modern data usage, their proactive approach to privacy and security will undoubtedly serve as a benchmark for other sectors to follow. This commitment to privacy innovation highlights the industry’s dedication to maintaining trust and integrity in its business practices, paving the way for a more secure and technologically adept future in construction.
Company Sample Data
Overview of Data
The dataset categorizes companies into five distinct size classes:
1. Micro (1 – 9 Employees)
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): 429.19
– Percent of Total: 11.88%
2. Small (10 – 49 Employees)
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): 1,168.50
– Percent of Total: 32.34%
3. Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees)
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): 1,134.79
– Percent of Total: 31.41%
4. Medium (200 – 499 Employees)
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): 420.23
– Percent of Total: 11.63%
5. Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees)
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): 172.85
– Percent of Total: 4.78%
Analysis of Trends by Company Size
The data indicates a pronounced trend where the bulk of the interest and engagement comes from smaller-sized companies, particularly those classified as Small (10-49 employees) and Medium-Small (50-199 employees). These two categories alone contribute to nearly two-thirds of the total engagement. This trend can be interpreted in several ways:
– Resource Allocation: Smaller companies might be more agile and able to pivot their strategies quickly to explore new technologies or compliance requirements related to privacy. They might also feel the immediate pressure of regulatory demands more acutely than larger firms.
– Innovation and Growth: Smaller to medium-sized firms often operate in growth modes where adopting the latest practices in privacy can be seen as both a differentiator and an enabler, helping to protect their businesses as they scale.
– Risk Perception: Smaller companies may perceive higher risk in non-compliance or security breaches due to limited financial and legal resources compared to larger enterprises that might have more robust systems in place.
Conversely, the relatively lower engagement from Medium and Medium-Large companies suggests that these entities might already have established protocols and systems for handling privacy, making them less likely to seek frequent updates unless significant regulatory changes occur. Additionally, these companies might be engaging in privacy-related activities through different channels or platforms not captured in this data.
Conclusion
This trend of heightened activity among smaller and medium-small companies highlights the critical role that size and operational scale play in how businesses prioritize and react to privacy challenges. It underscores the necessity for tailored solutions and awareness campaigns that address the specific needs and capabilities of companies based on their size.