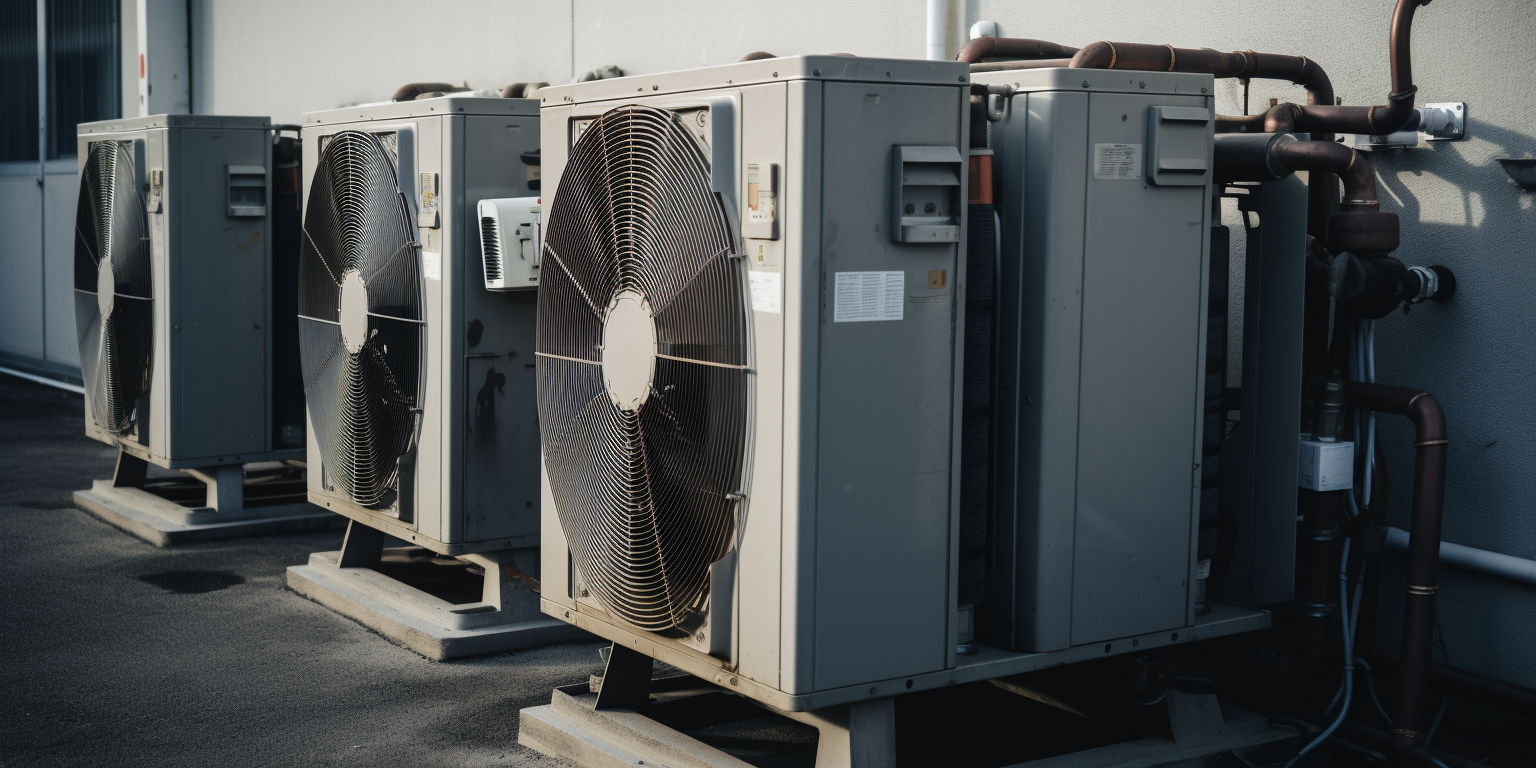
A Commercial Heat Exchanger is a handy device that plays a pivotal role in many refrigeration processes. Think of it as the peacekeeper in the realm of temperature control; its main task is to efficiently transfer heat from one medium to another.
To understand how it works, imagine a room full of people – some are hot, and some are cold. The Commercial Heat Exchanger steps in, acting like a good friend would, ensuring everyone feels comfortable. It takes the excess heat away from those who are hot and shares it with those who are cold.
In industrial and commercial refrigeration, the process is slightly more complex but follows a similar principle. The heat exchanger is often a set of tubes or plates. A refrigerant – a substance with a very low boiling point – circulates within these, absorbing heat from the environment or products that need cooling. As the refrigerant absorbs this heat, it evaporates, carrying the heat away.
Meanwhile, on the other side of the heat exchanger, a cooler medium – often water or air – is ready to receive this heat. As the hot refrigerant passes by this cooler medium, it ‘exchanges’ its heat, hence the name “Heat Exchanger”. The refrigerant cools down and condenses back into a liquid, ready to restart the cycle and absorb more heat.
What are the different types of Commercial Heat Exchangers?
In the realm of industrial and commercial refrigeration systems, a variety of Commercial Heat Exchangers are available, each designed to optimize heat transfer for specific applications.
First off, we have the Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers. These are the stalwarts of the industry, renowned for their robust design and high heat transfer efficiency. They consist of a series of tubes encased within a larger shell. The refrigerant circulates through the tubes, while the secondary fluid runs over the tubes inside the shell, allowing for efficient heat exchange.
Next, we come across the Plate Heat Exchangers. These devices make use of a series of thin, corrugated plates bundled together. The refrigerant and secondary fluid pass alternately between these plates, promoting effective heat transfer. Plate Heat Exchangers are particularly noted for their compact size and versatility.
The third type is the Coil Heat Exchangers. These are often used in air conditioning systems. They consist of a coil of tubes through which the refrigerant flows, while the air to be cooled circulates over the coils, extracting heat from the refrigerant.
Lastly, we find the Compact Heat Exchangers, designed for applications where space is at a premium. They offer high heat transfer efficiency within a small footprint, making them ideal for small commercial refrigeration units.
The selection of a Commercial Heat Exchanger depends on various factors including the nature of the application, space constraints, and the type of refrigerant used. Each of these types offers unique advantages, ensuring the most efficient heat transfer process for different refrigeration needs.
What are the key considerations when choosing a Commercial Heat Exchanger?
When it comes to selecting a Commercial Heat Exchanger for your refrigeration system, several key considerations come into play. First, let’s talk about capacity. You should match your system’s cooling demand with the heat exchanger’s capacity, ensuring it can handle peak loads without overworking.
Next, factor in the efficiency. A highly efficient heat exchanger uses less energy, reducing operational costs over time. Look for an exchanger with a high coefficient of performance (COP) – it shows the relationship between the cooling effect and the electrical energy consumed.
Thirdly, consider the compatibility with your current system. Make sure the heat exchanger fits seamlessly into your setup, taking into account the physical size, the type of refrigerant used, and the pressure ratings.
Maintenance needs are another aspect. Choosing a heat exchanger that’s easy to clean and maintain can save you time and resources in the long run.
Finally, don’t overlook the importance of the manufacturer’s reputation and warranty. Choosing a well-known brand with solid customer support ensures that help is available if you encounter any problems. The warranty period, meanwhile, provides a safety net against unforeseen faults or issues.
Remember, the decision to choose a heat exchanger should never be taken lightly. This is a critical component that affects your refrigeration system’s performance and efficiency.
What maintenance requirements are associated with Commercial Heat Exchangers in refrigeration systems?
Maintaining commercial heat exchangers in refrigeration systems is crucial to their long-term efficiency and reliability. In a proactive maintenance routine, you should start by regularly inspecting the heat exchanger surfaces for any dirt, dust, or grime. These particles, if accumulated, reduce the heat exchange efficiency by acting as unwanted insulators.
Next, keep an eye out for any signs of corrosion, especially if your heat exchanger is exposed to harsh conditions. If left unchecked, corrosion can lead to leaks, affecting the performance of your refrigeration system. Regular cleaning and scheduled protective coating applications can ward off corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan for your equipment.
Additionally, always monitor the performance of your refrigeration system. A sudden drop in efficiency may indicate potential problems with the heat exchanger. For instance, a clogged heat exchanger can cause the system to work harder, increasing energy consumption and leading to unnecessary wear and tear.
Periodic professional inspections are also worthwhile, as some issues may not be visible to the untrained eye. Experts can perform comprehensive checks, identify emerging problems, and recommend appropriate interventions.
Remember, preventive maintenance is far less costly than reactive repairs. By keeping your commercial heat exchanger clean, corrosion-free, and operating at peak efficiency, you not only ensure the reliable performance of your refrigeration system but also save on potential costly downtime and repairs.
What is the expected lifespan of a Commercial Heat Exchanger in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems?
A Commercial Heat Exchanger, an essential component in industrial and commercial refrigeration systems, typically boasts a lifespan that can span decades. It’s common for these rugged fixtures to last anywhere between 10 to 20 years, depending on the care they receive and the conditions under which they operate. However, just like any other mechanical device, a heat exchanger’s durability hinges greatly on maintenance and operational practices.
Regular maintenance plays a crucial role in prolonging the heat exchanger’s life span. By routinely cleaning and inspecting the exchanger, operators can identify and rectify issues promptly, preventing minor problems from escalating into major ones and ensuring the system continues to operate at peak efficiency.
In addition, operational conditions, such as the prevailing temperature and the type of media being cooled or heated, can also impact the heat exchanger’s durability. Heat exchangers subjected to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances might not last as long as those operating under more moderate conditions.
So, while a Commercial Heat Exchanger can traditionally offer a commendable service life in the realm of 10 to 20 years, it’s crucial to remember that regular maintenance and favorable operational conditions are key to realizing this longevity.
Are there any specific regulatory standards or certifications that Commercial Heat Exchangers must comply with?
Commercial Heat Exchangers must adhere to numerous regulatory standards and certifications to ensure safety, efficiency, and quality. These standards vary depending on the region and type of heat exchanger, but universally, regulations focus on efficiency, pressure capabilities, materials used and environmental impact.
In the U.S., specific certifications come from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). They offer the ‘ASME Stamp,’ a benchmark which signifies that the heat exchanger complies with the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC). This code covers design, manufacturing, and testing procedures, ensuring high standards of safety and reliability.
European heat exchangers, on the other hand, must adhere to the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) issued by the European Union. The PED encompasses safety regulations for pressure equipment, and compliance is mandatory for selling within the EU market.
Additionally, heat exchangers used in certain industries may require specific certifications. For instance, those used in the food and beverage industry often need to comply with Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations regarding material usage and hygiene.
Lastly, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides ISO 9001 certification, focusing on quality management systems. Heat exchanger manufacturers pursuing this certification aim to emphasize their dedication to quality and customer satisfaction.
How can software aid in the maintenance of Heat Exchangers?
Software can significantly assist in maintaining commercial heat exchangers, simplifying the process and ensuring optimal performance. With predictive maintenance software, for example, you can proactively manage your heat exchanger. The software monitors the system’s performance and uses data analysis to predict when maintenance is required. This way, you can schedule maintenance tasks before problems arise, preventing downtime and potential damage.
Additionally, software can provide detailed reports on the heat exchanger’s performance. These reports provide insights into aspects such as energy efficiency and system load, enabling you to make informed decisions about possible adjustments or improvements.
Moreover, software solutions can offer troubleshooting guides, helping you identify and resolve common issues swiftly. You no longer need to rely solely on expert technicians, which can be a significant time and cost saver.
Lastly, the use of software can streamline the documentation process. All the necessary information about maintenance, such as service schedules, parts replaced, and performance data, can be stored digitally. This makes it easier to access and review the information whenever needed, ensuring seamless maintenance operations.
In a nutshell, software can be a powerful tool for commercial heat exchanger maintenance. It offers a proactive, data-driven approach that not only ensures the longevity of your equipment but also improves its performance and efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
- A Commercial Heat Exchanger, a crucial component in commercial and industrial refrigeration systems, can last between 10 to 20 years, depending on maintenance and operational practices.
- Regular maintenance is key to prolonging a heat exchanger’s lifespan, helping to identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
- The lifespan of a Commercial Heat Exchanger can also be influenced by operational conditions like temperature and the type of media being cooled or heated.
- Commercial Heat Exchangers must adhere to various regulatory standards and certifications for safety, efficiency, and quality. These include ASME Stamp, Pressure Equipment Directive (PED), FDA regulations, and ISO 9001 certification, among others.
- Software can significantly aid in maintaining Commercial Heat Exchangers by predicting maintenance needs, providing detailed performance reports, offering troubleshooting guides, and streamlining documentation.