Executive Summary: Commodity Research Trends in the Construction Industry
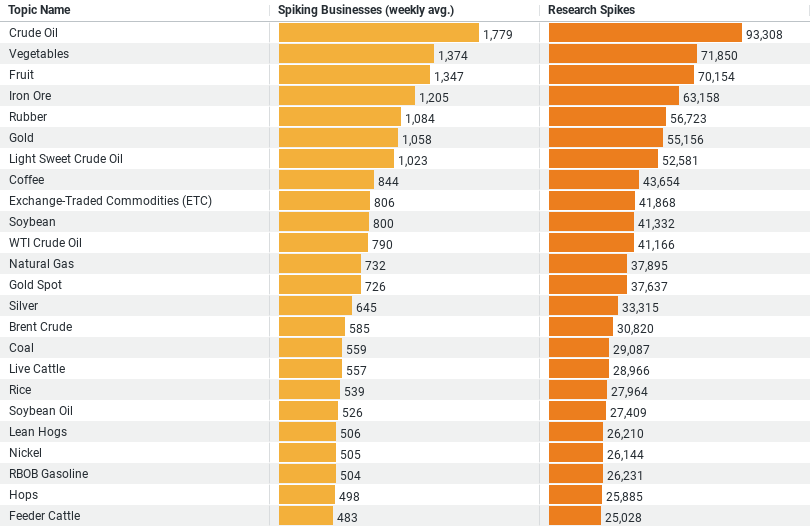
– Crude Oil: Dominates interest with a weekly average of 1,778 businesses showing heightened activity and a total of 93,308 research spikes, making it the most researched commodity.
– Vegetables and Fruit: These commodities also show strong research interest, with vegetables attracting 1,374 businesses weekly and fruit 1,347, having total research spikes of 71,850 and 70,154 respectively.
– Iron Ore and Rubber: Critical for construction materials, these commodities show significant research engagement, with iron ore attracting around 1,205 businesses and rubber 1,084 weekly, alongside research spikes totaling 63,158 and 56,723 respectively.
Commodity Research Trends in the Construction Industry
The construction industry is a dynamic sector heavily influenced by the fluctuations and trends of various commodities. Recent data provides fascinating insights into which commodities are currently the focus of research and strategic interest within the industry. Understanding these trends is crucial for industry stakeholders to anticipate shifts in material costs and supply chain dynamics.
Crude Oil: A Central Focus
Crude oil is undeniably the most researched commodity in the construction industry. The data reveals an average of 1,778 businesses per week showing increased interest or activity in this commodity, with a total of 93,308 research spikes noted. This intense focus on crude oil is understandable given its critical role in not only fueling the machinery necessary for construction projects but also in the production of numerous construction materials. As oil prices fluctuate, so too do the costs associated with transport and synthetic materials, such as plastics and asphalt, which are vital to various construction processes.
The high level of interest in crude oil highlights the construction industry’s sensitivity to global oil markets. Companies seem to be continually monitoring these markets to mitigate risks associated with price volatility, which can significantly impact project costs and timelines.
Agricultural Commodities: Sustainable Building Trends
Following crude oil, vegetables and fruits are the next most researched commodities, with weekly averages of 1,374 and 1,347 businesses respectively engaged in research, and significant spikes in research activities tallying 71,850 and 70,154. The prominence of these commodities may seem unusual in the context of construction. However, this likely reflects a growing trend towards sustainable and eco-friendly building practices that incorporate green spaces and agricultural elements into building designs.
This interest also suggests that the construction industry is exploring more sustainable supply chains and considering how factors like food production can be integrated into urban development projects. For instance, the use of green roofs and edible gardens within residential and commercial buildings is an innovative approach that could redefine urban living spaces.
Industrial Commodities: The Backbone of Building
Iron ore and rubber also feature prominently in industry research, with iron ore attracting around 1,205 businesses weekly and rubber 1,084. These commodities are staples in construction, fundamental for producing steel and providing various building materials used across all types of construction projects.
The focus on iron ore aligns with the industry’s need for durable and robust materials like steel, which forms the backbone of major construction frameworks. Rubber, meanwhile, is researched for its applications in insulation, roofing, and flooring materials. The demand for research into these commodities underscores the ongoing need to optimize material properties for safety, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Implications for the Construction Industry
The insights from the data are clear: the construction industry is deeply entrenched in the commodities market, with strategic research focused on both traditional and innovative materials. This research is not merely academic; it directly impacts business strategies, project planning, and risk management.
Companies within the construction sector must continue to monitor these trends closely. By understanding which commodities are attracting the most research and why shifts in interest occur, businesses can better navigate the complexities of global supply chains and material availability. Additionally, by staying informed about sustainable practices and innovative uses of materials, companies can enhance their competitive edge and appeal to a market increasingly concerned with sustainability and innovation.
In conclusion, the construction industry’s keen interest in commodities like crude oil, agricultural products, iron ore, and rubber highlights its complex relationship with global markets and its impact on everything from operational costs to sustainable development. Keeping a pulse on these trends is crucial for anyone involved in the sector, from project managers and developers to investors and policymakers.
Company Sample Data
– Company Size: Categorizes companies based on the number of employees. The categories range from micro enterprises (1-9 employees) to large enterprises (over 1,000 employees).
– Spiking Businesses (weekly avg.): Reflects the average weekly number of businesses within each size category that have shown a marked increase in activity or interest in a particular area.
– Percent of Total: Represents the percentage of total spikes attributed to businesses of each size category.
Data Summary by Company Size
– Micro (1 – 9 Employees): These companies account for approximately 11% of the total spikes, with an average of about 1,129 businesses showing significant interest weekly. This suggests that even the smallest companies are actively engaging in market trends, possibly due to the agility and niche focus many micro-enterprises possess.
– Small (10 – 49 Employees): Small companies represent about 28% of the total spikes, with around 2,903 businesses each week. This size category is likely to be more established yet still flexible enough to adapt quickly to new opportunities or shifts in the market.
– Medium-Small (50 – 199 Employees): This group leads with the highest percentage of interest at approximately 30%, averaging 3,098 spiking businesses. Businesses of this size may have enough resources to allocate toward research and development or market exploration, positioning them to capitalize on emerging trends.
– Medium (200 – 499 Employees): These businesses contribute to around 14% of the total spikes, with about 1,429 weekly. They likely have more structured processes and might focus on sustained growth in specific areas of interest.
– Medium-Large (500 – 999 Employees): At about 7%, this category has 697 businesses showing a weekly spike in interest. These companies are possibly focusing on consolidating their market positions and might be less reactive to market fluctuations compared to smaller entities.
Trend Analysis Depending on Company Size
The trend of varying levels of activity across different company sizes may be influenced by several factors:
– Resource Allocation: Larger companies often have more resources to invest in broad market research but may be slower to adapt due to their size and internal processes. In contrast, smaller companies can quickly pivot and adapt to new opportunities, though their market influence may be limited.
– Risk Tolerance and Market Focus: Smaller companies might pursue niche markets or innovative projects as they seek rapid growth, while larger companies may focus on enhancing their positions in established markets, balancing risk more conservatively.
– Agility versus Stability: Smaller companies typically exhibit greater agility, enabling them to spike in research and development activities quickly. In contrast, larger enterprises may exhibit steadier, less volatile activity spikes due to their focus on long-term stability and gradual innovation.
The insights from this data suggest that company size significantly impacts how businesses engage with market trends, affecting their research intensity and areas of focus. This analysis could help stakeholders across all sizes to benchmark their activities and strategize their market positioning more effectively.