Reports from 2022 to early 2025 on the field service management market agree that the field service management industry is already massive, with an average estimated value of $4.5 billion USD. And projections say it’s only going to get bigger – on average, they see it more than tripling in value to about $15 billion USD by 2033. The message is clear: more industries and trades around the world are adopting software and other tools to coordinate their field service activities.
So what is field service management ? Why are field service companies increasingly investing in it to help manage their operations both at job sites and in the back office? How can your field service business use it effectively? And what are the best tools to use for helping you manage your fieldwork most efficiently? This article will be your guide.
- Fundamentals and essentials of successful field service management
- Mastering the 9 key components of the field service management process
- 10 field service management best practices
- How to measure the effectiveness of your field service operations
- Top 5 field service management software tools for contractors
We’ll start by covering some basic things you need to know about field service management before we dive into the details.
Fundamentals and essentials of successful field service management
To be successful in field service management (FSM), you need to first understand what it is. This section will:
- Give a field service management definition
- Break down what field service management (FSM) has to actually manage
- Give some advice on being a good field service manager
- Highlight some common problems you may run into when managing field services
- Explain why using software to automate field management processes is so useful
What is field service management?
Field service management is the set of processes companies use to coordinate work they do at customers’ properties, including installations, repairs, maintenance, and removals. This means deciding which field resources – techs, equipment, and vehicles – need to be where, when, and working on what. It also includes planning routes to job sites and monitoring techs in other ways to make sure everyone is executing their roles efficiently.
Field service management also involves making a framework for how to deal with customers. This includes how to find customers looking to hire and marketing your services to them, and estimating or quoting how much a project will cost. You also need to work with customers to schedule field visits, update them on project progress, answer any questions or special requests, and consider any feedback they give you – ideally giving them an online portal to do some of these things themselves.
Finally, you have to invoice clients for your services and make sure they pay in a timely manner so you have the money you need to keep running your business.
What are FSM operations made up of?
FSM operations involve tracking information and giving direction along all points of a field service company’s customer lifecycle. That includes marketing & sales to reach customers, managing field work so jobs get done right, and customer relationship management to build brand loyalty.
In short, FSM (field service management) is made up of a number of different processes, including:
- Marketing, lead generation, and customer acquisition
- Price estimates, quotes, and sales
- Scheduling field service visits and dispatching technicians
- Managing field service vehicle use and choosing optimal routes to job sites
- Tracking job progress, tech time tracking, and resource locations
- Invoices and billing for field service work performed
- Customer relationship management (CRM) and arranging future service calls
What does a successful Field Service Manager do?
A successful field service manager is a leader on two different fronts. On the field operations side of things, they need to coordinate work at a job site so a project is done properly, efficiently, and on time. On the CRM side of things, they work to keep customers happy by updating them on job progress, answering questions, addressing concerns, and negotiating deals.
So a field service manager has to be good at things like:
- Leadership – A field service manager must have the courage to take control of situations and make tough decisions. They also should be able to settle disputes diplomatically.
- Problem-solving – Field managers should have an eye for detail that helps them identify a potential problem at a job site, assess its context, determine its root cause, and come up with a plan to solve it.
- Teamwork – Ultimately, a field service manager is still part of a team. So they should be open to considering ideas and accepting other kinds of help from team members.
- Team member management – Field managers should know how to get the most out of the people they’re working with. That includes assigning tasks at a job site so everyone is working on something they’re good at (or at least capable of doing). It also means recognizing techs who go above and beyond in their work and stepping in to help if a tech is struggling with a task or unexpected problem.
- Interpersonal communication – This skill not only helps field service managers collaborate better with their teammates, but also helps them provide better customer service. Understanding customer needs by effectively listening to them and providing solutions quickly helps drive customer loyalty, which helps increase sales and profits.
- Multitasking – Field service managers have to juggle many tasks at once: directing field techs, coordinating resource & equipment use, stepping in to solve tough problems, and providing progress updates to both head office and customers. So they need to be able to prioritize which tasks to focus on first, and how much attention can be given to each task before the manager needs to move on to something else.
Common challenges in field service management
Running a field service company is rarely simple, and comes with many different pressures that field service companies have to overcome and adapt to if they want to remain competitive and stay in business. Some common ones include:
- Setting standard procedures – A big part of how efficient a field service company works is how well employees know what they’re responsible for, how they need to do things, and what they have to record about their work. This can be tricky because each job they take on has different conditions that forces them to adjust how they work on the fly.
- Maintaining quality & compliance – Field service companies have to meet safety and quality benchmarks set by regulators to avoid legal trouble. They should also follow these guidelines so customers are more satisfied with the work done. However, doing so may call for extra expenses to buy new or improved equipment, which can make it tougher for contractors to turn a profit.
- Balancing costs and revenue – Another hurdle to profitability for field service companies is maintaining competitive pricing while keeping costs down. Field service companies want to keep their parts & labor prices around the industry average because if you’re too expensive, people won’t be able to afford you, and if you’re too cheap, customers think you might not do a good job. This all has to be weighed against the costs of paying admin people & techs and buying/repairing/replacing parts, equipment, vehicles, and field service management systems.
- Meeting changing customer expectations – More and more, customers are counting on companies (and not just those in the field service industry) to cater to their specific needs. Their overall expectations are rising as well in terms of things like how quickly they’re served, how often they’re updated on job progress, and how private their data is.
- Keeping up with new technology – Technology evolves so rapidly these days that it’s hard for a field service company to pick out what might be useful to them and adopt it quickly enough to keep up with competitors. The adoption process can be a challenge by itself, as new technologies may not neatly fit into a field service company’s existing tech stack.
Benefits of automating your field service operations
One of the key reasons to use technology in managing field service operations is it can automate certain tasks: doing them faster, with less chance of error, and without needing an actual person involved. Here are some specific ways that can support your field service team:
- Less manual admin tasks means saved time – Nobody likes doing paperwork, so get technology to do it for you. Field service management software makes it easier to input relevant field data or even collect it automatically, then instantly fill it into documents like reports and invoices. Less time doing admin work by hand means more time doing things that help your company profit.
- Automatic planning of maintenance schedules – Based on data concerning how long a customer’s equipment usually lasts, technology can automatically pick future dates for techs to come in and do maintenance. This simplifies scheduling, reduces the chance you’ll need to do costly emergency repairs, and overall serves the customer better.
- Streamlining financial functions – Your business can’t function without money in the bank. And you can’t get that money until you bill your customers after a job is done. According to our research, the invoicing sweet spot (best time to send your invoice to a customer) is within 10 days, as sending later increases the average time it takes to get paid rises significantly. Automating tasks like estimating, invoicing, and processing payments all from one FSM platform helps you get the money you need to cover your expenses quicker.
- Centralizing & organizing relevant data in one system – The days of rummaging through filing cabinets and leafing through file folders to find a document you need are over. FSM software allows you to gather all information your company needs – on techs, customers, equipment, finances, and so on – in one place, and arranges it so it’s easy to both access and search.
- Use field data to improve business operations – Automatically collecting and analyzing data on your field service operations lets you more accurately estimate metrics like how long jobs will take and how much your resources cost. This not only helps you budget your time and money wisely, but also lets you spot areas where your company could be more efficient and cut costs.
- Fewer admin mistakes from human error – No matter how good they are at their jobs, humans are eventually going to make mistakes. It’s a fact of life. But you don’t want a mistake to cost you money because a document was filled out wrong or cost you time from having to redo work. Automating tasks through FSM software, if done correctly, makes errors far less likely because tasks are done by a computer just doing exactly what it’s programmed to do.
- Developing tech training plans – Another way you can use data is to see how your techs are performing. You can recognize and reward techs who are performing well, or send techs for more training if they aren’t performing up to standards. Also, you can look at data to see what kinds of jobs you get most often (especially if you’re a multi-trade contractor). Then, either through training or hiring, you can make sure you have enough techs on staff who can handle your most frequent job types to keep any one tech from burning out.
Mastering the 9 key components of the field service management process
There are many tasks that go into delivering field services. You have to find customers and market your business to them. You need to give customers estimates on what their projects will likely cost. You have to schedule service visits when you have time and technicians available. You need to actually get techs to the correct work site on time. You have to monitor the work site to make sure your techs are completing a job efficiently and none of your equipment goes missing. You may need to set up further appointments for recurring maintenance. Finally, you have to invoice customers for your work and make sure they pay you promptly.
All of these tasks form a long and complicated cycle where they feed into each other, so you have to be good at each of them for your field service company to work properly. Focusing on one at the expense of the others isn’t going to cut it. In that light, we’re going to break down what it takes to succeed at each of the 9 major processes in field service management.
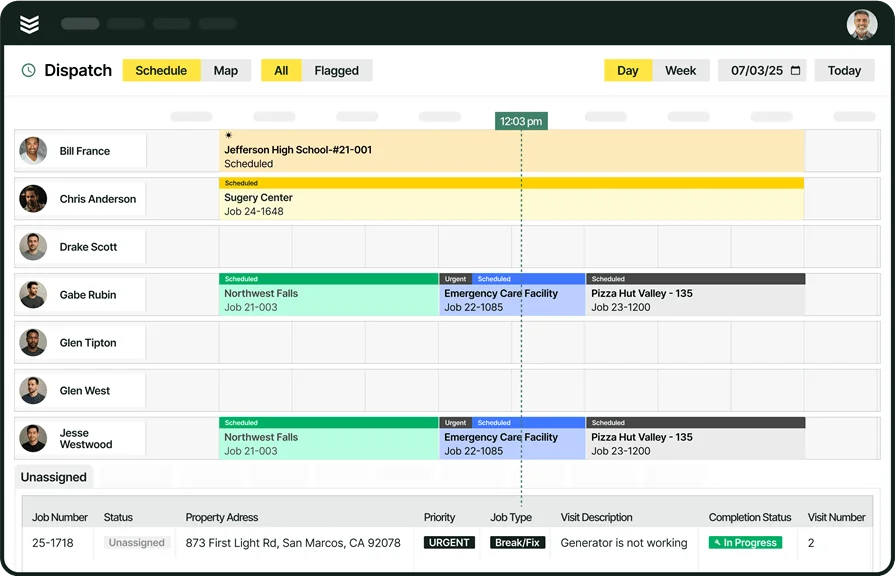
1. Field service scheduling & dispatching
Field service scheduling & dispatching involve choosing a date and time to send field techs to a job site, and then notifying techs where they need to go and when.
Dispatchers need to make sure the right techs are sent to the right service calls, and keep field service schedules flexible to allow appointments to shift if an emergency happens or a customer cancels at the last minute. This means making sure the techs being scheduled are qualified, available, and there are enough time gaps between their assigned jobs so they don’t get overworked.
Dispatchers also need to make sure techs get to jobs efficiently and prepared to work. That means scheduling jobs for a tech or team of techs so they’re at locations close together, cutting down on travel time and costs. It also means sending techs information about inventory status and even the customer’s past service calls so techs will know they have the parts they need and an idea of what the situation is before they’re even at the job site. Finally, they need to schedule jobs at predictable times, track tech locations, and keep customers informed so they have reasonable expectations.
Technology can help here. Field service scheduling software can automatically analyze your technicians’ availability, skillsets, workloads, and service call routes to slot in appointments where they make sense. Meanwhile, field service dispatch software helps you know where your techs are and where they need to be at all times. This lets you easily fill in time gaps with a new job assigned to an available tech if a customer cancels last-minute. It also allows you to efficiently shift job times and assigned technicians around if something urgent comes up.
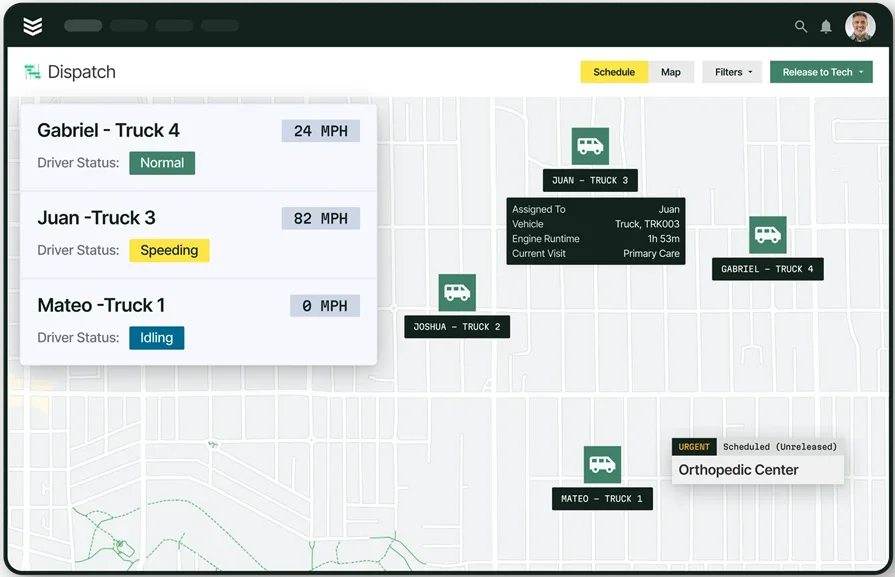
Dispatching is the foundation
See how BuildOps Smart Dispatch can save you hours of manual time each day.
2. How to track field employees
Tracking field service techs while they’re on the job makes sure they are at a work site doing their job when they’re supposed to be, lets your back office staff know how a job is progressing, and tells you where a tech is if they need assistance or are in distress.
As for how to track field employees, you can use a combination of GPS tracking, geofencing (creating a virtual barrier around an area that tracks whenever someone crosses it), and SIM-based tracking using your techs’ cell phones.
Another way to track employees is by setting up dedicated company Internet networks, and having techs sign up for work-only accounts on company-approved communication tools. This keeps your techs inside your own network and keeps others out, reducing the risk of a data breach. It also allows you to monitor their Internet usage to make sure it’s being used productively.
Just make sure to get your techs’ explicit permission before you track them. Let them know how the tracking equipment or apps work, what data you’re collecting, and what that data is being used for. If you track them without consent, or track a type of data you didn’t tell them you were going to track, it can get you in deep trouble with regulators and the law.
3. Time tracking for field techs
Just as important as tracking where your employees are is tracking how long they’re there. Time tracking for field technicians involves recording when they enter or leave a work site, how long they stay at a work site, how long their breaks are, and how long it takes them to get from one job site to the next.
As for why you want to track these things, they help you do things like:
- Pay your techs fairly for the work they do
- Know when a tech is late to a service call, taking too long on break, or otherwise not being productive
- Confirm when a tech is working overtime so you can pay them accordingly
- Estimate how long it takes to complete a task or job, letting you measure the efficiency of your processes
- Optimize routes techs take between service calls to provide faster service and cut fuel costs
Ideally, you want to track time in real time. The more closely you track it, the better you’ll be able to resolve questions and conflicts regarding where an employee was at a certain time and how long they were there. You can do this by simplifying or automating time tracking by using GPS signals or geofencing, or allowing techs to track their own time in the field through a mobile app.
You should use time tracking software for field service techs that does two things. First, it should have reporting and analytics functions that can calculate time-related totals and averages for individual techs – and your entire team of techs – over a given time period. These stats include hours worked, time spent on tasks or jobs, time spent traveling, work time counted as overtime, and idle time or downtime. With this data, you can determine things like:
- Which techs are being more or less productive
- How efficient your fieldwork procedures are
- Which routes will reduce overall time spent travelling between work sites
- How fairly your dispatchers are balancing workloads in their scheduling
Second, the time-tracking in your FSM software should integrate with other features like accounting and project management. An integration with accounting functions allows them to automatically determine how much to pay staff based on the number of work hours they logged, helping to prevent payroll fraud.An integration with project management allows them to adjust expected project schedules based on the pace of work, and shift task assignments to give more important tasks to techs who are putting in the extra effort.
As a bonus, these integrations often mean you don’t have to manually enter the same data in multiple places, saving time and avoiding inconsistencies.
4. Field service asset & fleet management
Field service asset management refers to tracking the locations, conditions, and quantities of the physical equipment you use in fieldwork, including inventory and fleet management.
Inventory management is monitoring how many parts, tools, vehicles, and other pieces of equipment your company has to complete field service jobs with. Ideally, you should automate this process with FSM software so you can instantly order more of something when its stock dips below a certain level. This helps you know that if an urgent job comes up, you have the assets you need to handle it ready to go.
Another good practice for inventory management is to track larger pieces of equipment just like you track employees. One benefit of this is you can know where the equipment is if it gets left at a work site or even stolen. Another benefit is that, in an emergency, dispatchers can locate relevant assets nearby and quickly send them to fix the problem faster and limit the damage it does.
Fleet management refers to supervising and improving all aspects of using vehicles for your fieldwork. With fleet management software, you can track where your vehicles are – not only if they’re taken places where they shouldn’t be or stolen, but also if they’re close to a work site needing help so you can send the nearest ones over quickly.
Fleet management can also track the routes vehicles take between work sites, and the time it takes to navigate those routes. This helps dispatchers because it lets them schedule appointments for a certain tech at work sites close together. This cuts down on the tech’s drive time, saving fuel costs and giving customers more prompt service. It also lets dispatchers provide customers with estimated arrival times for techs or crews at work sites so customers know what to reasonably expect. Additionally, it allows for monitoring how techs drive so you can identify unsafe driving habits – like speeding or braking too hard – and work with techs to get rid of them.
Fleet management can also track the condition and fuel levels of vehicles. This helps you schedule preventative maintenance to keep your vehicles running well and avoid them breaking down, potentially stranding your techs. It also lets you plan when techs need to refuel, preventing fuel fraud and other unauthorized expenses by comparing the amount of fuel in a vehicle to how much was actually purchased.
5. Maintenance scheduling
Maintenance scheduling involves planning times to repair equipment – including replacing its parts, if necessary – to avoid it failing at a critical time. So part of inventory management should be tracking how long it takes before equipment starts to break down. Then schedule preventive maintenance – starting with the most important assets for your work – at intervals shorter than these times to keep the equipment functioning. Be sure to also account for seasonal conditions when doing this, too.
Another helpful maintenance scheduling practice is to make your field techs aware of maintenance schedules. If they know when they will or won’t be able to use certain equipment, they can work around those schedules to minimize work disruptions. It’s also a smart idea to schedule routine asset inspections so you can catch problems if an asset’s condition worsens faster than expected. Finally, keep records of all maintenance work you do. This not only helps in auditing, but also lets you track what tends to go wrong with certain assets so you can be ready to quickly fix those issues.
6. Field routing optimization
Field service routing consists of finding the most efficient way to get techs to different work sites and then back to the office. This isn’t as simple as it may sound, though – it requires scheduling, dispatching, fleet management, and time tracking processes working together.
The scheduling part requires determining which service calls need to be dispatched to the earliest based on their urgency and location. Additionally, dispatchers must factor in the availability of techs with the necessary skills to complete the work. Then comes the dispatching part: figuring out the most efficient route between each tech’s scheduled service calls that day, and relaying this information to your techs.
Ideally, you’d use FSM software to automate these processes. Automating scheduling helps to line up each tech’s assignments so it’s easier to find an optimal route for them when dispatching. It also helps balance your team’s workload so none of your techs are taking on too many jobs without enough downtime in between. Automating dispatching, meanwhile, allows you to send information about service calls – including the best routes to take to the job sites – to techs as soon as jobs are scheduled and locked in. This reduces the amount of time your techs remain idle between service calls and helps them get to job sites on time more often.
The fleet management part is about monitoring your techs while they’re on the road and adjusting their routes to account for unexpected delays. For example, heavy traffic or construction can slow down an otherwise faster route. Or part of a route may be completely blocked off by a road closure or a traffic accident. It’s important for dispatchers to keep an eye on these kinds of events as they develop, determine what the next fastest route would be, and communicate this information to techs on the road in real time.
The time tracking part involves measuring the actual amount of time your techs spend in transit and at work sites. This not only provides data you can use to more efficiently plan routes, but also shows how productive your techs are. This, in turn, lets you accurately calculate payroll and make sure jobs get done on time.
The value you get from all this is that the right techs get to the right jobs faster and work more productively, allowing you to get more jobs done in a day. It also helps evenly distribute workloads so techs don’t get overworked. Furthermore, you save money on fuel, vehicle maintenance, and having to pay overtime for techs to get jobs done on time. And all of this leads to happy customers who appreciate how quickly they’re served and how expertly the work is done.
7. Estimating & pricing your field services
Field service pricing is about setting the rates and costs for your work, including labor, travel, materials, and other expenses specific to the job, industry, or location. These rates factor into an estimate (your best guess at what the job will cost) or a quote (a locked-in amount you plan on charging).
When setting these rates, you should think about all corresponding expenses related to completing a service call:
- How much you’re paying your techs
- How much the parts you need to install or replace cost
- How much the necessary equipment to install, repair, or replace parts costs
- How much you spend to buy vehicles and keep them fueled to travel between work sites
- How long the work is expected to take
- What possible issues might arise that could increase costs or timeline
- Any other expenses that may be unique to your industry or where you operate
You should also compare your rates with competitors to see if yours are in a fair range. If they’re too low, you won’t turn a profit, but if they’re too high, customers may opt for a cheaper alternative to you. Remember to check customer demand metrics and overall market conditions frequently – these can also give you signals on whether you should adjust your prices up, down, or not at all.
Ideally, you want to use estimating software for commercial contractors to automate all of this. It can automatically calculate rates to line up with competitors, market conditions, and customer demand. It can also automate estimating and quoting to avoid errors and give customers clear pricing, which helps move the sales process along.
8. Invoicing, billing, & payments for field work
Even if you estimate or quote a price for your work, you still have to make sure the customer pays it. This means creating an invoice, sending it to the customer as a record of you billing them for the work you did, giving the customer various options to send payment, and following up with customers if you don’t receive payment.
Field service invoicing software can automatically create and send out invoices based on your rates, what parts were used during a job, and any other costs indicated in field reports. This keeps your pricing straightforward, eliminates the chance of mistakes, and gets bills out to customers earlier. This helps you get paid faster because customers tend to pay quickly if you send an invoice out shortly after a job is finished. You also won’t have to waste time disputing charges with customers. And you can send automated reminders to customers who haven’t paid their invoices they still owe you money.
Meanwhile, field service payments software can integrate with different payment processing systems so customers can choose a payment method convenient for them. It can also connect to your accounting system so payment data automatically gets recorded in your books without you having to enter it manually, saving time and avoiding mistakes.
9. New customer acquisition & pipeline generation
You can’t always rely on your existing customers to keep money coming in. You need to seek out new opportunities and spread the word about why your contracting company is the best fit for any number of jobs.
That’s where lead generation software like BuildOps CRM & Pipeline tools comes in. You can use it to automatically retrieve information on potential customers and jobs that match your business’s specializations and capabilities.
It can also automatically organize or filter those data points based on the project’s estimated value, whether the person or organization requesting the project is actively looking for help, and so on. This helps you focus on gaining new customers who are actively interested in hiring contractors like you, have a job or project that fits with what your business can do, and will pay you enough for that job or project for you to make a profit.
10 field service management best practices
We’ve gone over how to better manage specific field service components. Now, we’ll give you some high-level field service management best practices that cover general advice on how to optimally manage your field service company – both in the field and in the back office.
1. Digitize as much as possible while maintaining data security
Physical paperwork is inefficient. Writing things out by hand is slow, and filing countless documents away in folders and cabinets takes up space and money. You also don’t want to have to go chasing after your techs or have them return HQ for a pit stop because they forgot the information documents for a service call. That wastes time and fuel (if they’re using a vehicle), and the alternative isn’t any better: you look bad in front of customers when your techs show up for a job not knowing what to do.
Digital paperwork is much easier to store, organize, secure, move, and even access remotely. This saves you a lot of time and overhead, and reduces the risk of information containing errors or getting lost. Just be sure to invest in technology and training to keep sensitive information about your customers, staff, company, and projects secure. Also keep up with current privacy standards and cybersecurity regulations, as rules and best practices change frequently.
2. Use a field service CRM
Knowing your customers is critical to being successful in the field service industry. And we don’t just mean taking down their contact information so you know how to reach them or who to bill. Information like their history of service calls and any feedback they give through surveys, phone calls, emails, social media, and so on is valuable as well.
By knowing what work your customers have had done before, you can suggest future work they should get done (like recurring maintenance or an eventual upgrade). Customer feedback can also be a way to reward techs for exceptional service or see how your field service could be improved.
It’s also vital to know who potential customers are and what they’re asking for so you know a job you’re bidding on is within your team’s skillsets and capabilities. And you should make all of this information available across all of your departments so everyone on your team can use it for their unique jobs.
Expert Tip
In short, you need a field service CRM. And what we’ve talked about here just scratches the surface of what BuildOps’ CRM+ for Commercial Contractors can do. Check it out!
3. Set up customer hierarchies to enable smoother operations
Especially in commercial environments, a customer may own more than one property. This can create issues for field service companies because the owner may not be the one who actually manages each property. You might even need to contact a different manager for each property. If you don’t get in touch with the right person, they won’t have the property ready for you to work on when you show up because they didn’t know you were coming.
With customer hierarchies, you can instantly see the link between a customer and all the properties they own. This lets you confirm you’re working on the right property, are contacting the right manager, and billing the right customer. It’s also helpful if you need to remember information specific to a particular property, such as access codes or other security clearance you need to get into the building or certain sections of it. This saves time if you have to visit a property again for repeat visits or future jobs, as you’ll know how to get in and out of buildings outside of working hours without needing to ask the building contact person.
4. Focus on your customers
Your customers are ultimately the ones who determine whether your business succeeds or fails, so treat them right. Personalize your communication with them as much as possible. Give them online self-service portals where they can manage their accounts, book appointments, and pay invoices. Send them automated reminders of upcoming appointments or unpaid bills. Allow them to see in real time how close techs are (in both time and distance) to the work site, and give them updates on how the job is progressing.
Customers generally want you to make things easy for them, be honest with them, and do your work efficiently. Being upfront with them and keeping them in the loop helps to manage their expectations. You should also encourage them to write reviews or give other feedback, and give them channels they can easily do this through. If you notice patterns of customer expectations not being met in any area of your business, that’s a sign you’ve got something to fix.
5. Optimize scheduling & dispatching
Scheduling & dispatching are extremely important to get right for your field service company. They directly impact things like how many jobs you can do in a day, whether your techs make it to the right job site prepared and on time, and whether your techs are equally sharing your available jobs.
Invest in scheduling & dispatch tools that factor in things like tech skills, availability, and overall workload, potential job length, and distance between job sites. These let you automatically slot in service calls where they make sense and assign techs who can handle the work in terms of both their capabilities and stamina.
6. Give techs mobile tools to use
According to a 2021 study, 99% of field service techs use a mobile phone to aid their work. Take advantage of that by giving them mobile apps so they have greater capabilities right in the field and don’t need to return to HQ so often. They can do things like write reports, create invoices, collect signatures, take photos, accept payments, and find faster travel routes without needing extra equipment. They can also maintain real-time contact with dispatchers to provide updates, ask for help, or get notifications of new assignments.
Finally, they can remotely access a central database that contains information like job details, equipment manuals, and troubleshooting guides. This allows them to problem-solve on site, helps improve their first-time fix rate and cut down on repeat visits that cost you time and money.
7. Use real-time tracking tech
Tracking your techs, vehicles, and other equipment in real time using GPS, geofencing, and SIM cards is useful for a number of reasons. It lets you:
- Pick the most efficient routes for techs to take to work sites, including avoiding traffic, accidents, or construction
- Show customers waiting for techs to arrive where the techs are and roughly when they will be at the work site
- Tell you when employees enter or leave a work site, helping to prevent “buddy punching” fraud
- Track work and break time accurately while techs are at work
- Find equipment if it’s left at a work site, stolen, or used for unauthorized purposes
- Precisely locate your techs in an emergency
8. Move towards proactive inventory management
It’s said that if something isn’t broken, you shouldn’t fix it. We disagree. Working proactively to keep equipment from breaking down or inventory stock from running out not only reduces maintenance costs, but also guarantees you have backup resources available if something goes wrong.
If you reactively wait until a piece of equipment breaks or you run out of parts, it will likely cost much more to repair or replace these resources. You may also have to reschedule or cancel some service calls because you don’t have what you need to complete them – or at least call in other techs as emergency backup. This costs you revenue and wastes your time, and it also frustrates your customers – which can cost you future sales, too.
9. Monitor metrics and make data-driven decisions
Collect data on various parts of your business – after you get consent, of course. Ask questions like:
- How long is it taking techs to get to job sites?
- How long is it taking techs to finish their jobs?
- Which techs are putting in the most work?
- How much revenue do service calls bring in versus what you have to spend in wages, travel, and inventory to complete one?
- How fast do you typically run out of certain parts, and how long on average does specific equipment work properly?
- Which parts of your service are your customers satisfied or dissatisfied with?
- How much is it costing you, on average, to bring in new customers?
- How many of your customers give us repeat business?
Gathering data to answer questions like this will, over time, reveal patterns that help you make more informed decisions on how to optimize your field service processes.
10. Never stop learning
Every day, it seems there are new technologies and techniques to help with doing just about anything – including field service projects. That’s why it’s important to regularly research and train your employees on new tools and methods so they can improve their productivity and be better prepared for unfamiliar things they may see at a worksite. It can also be useful to train employees on soft skills to make them more effective in their other work tasks.
How to measure the effectiveness of your field service operations
You can’t be everywhere at once in your field service company to see exactly how the work goes, especially with your techs spread out at different job sites. That’s why you need another way to “see” it: interpreting data from reports your techs bring in from their fieldwork and reports your back office staff create. Over time, you might see trends of where your company is going strong and where it could be doing better.
This section will go over field service reporting: what things are important to measure about your company and what they mean.
Top 5 field service metrics & KPIs to measure operational performance
To know what your field service company’s strong and weak points are, you have to first gather the data and interpret it in a meaningful way. Here are five key ways to interpret the data you collect from your operations:
1. Technician Utilization Rate
This measures how much time a tech spends completing service work as opposed to some other part of their job (e.g. travel, admin tasks, or idling or waiting for resources to arrive). It’s calculated by dividing the total time a tech is working on billable tasks by the total time they’re on duty, then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage. A low number can point to issues with your scheduling, dispatching, routing, or other internal processes. Or it may be a case of your tech not being properly trained or productive enough.
2. Average Service Call Value
This is the average amount of revenue you earn from each service call you complete. Calculate it by dividing the total revenue from completed service calls by the number of booked service calls over the same time period. You can increase this number by adjusting your pricing rates or training your techs on how to upsell and cross-sell (including recurring and post-warranty maintenance). You can also improve scheduling & dispatching effectiveness and technician productivity to avoid no-shows, preventable rescheduling, and repeat visits that cost you money.
3. Customer Acquisition Cost
This is the average amount of marketing & sales money you have to spend to get a new customer to request and complete a service call. It’s calculated by dividing your total marketing & sales expenses by the number of new customers who use your services over the same time period. A high number may suggest you need to shut down underperforming campaigns and try new ones that reach customers over different channels, and that have content personalized for particular groups or even individual customers.
4. Service to Cash Rate
This measures the average amount of time it takes a customer to pay an invoice when you send it out after a service call. In other words, it’s when money you’re owed turns into usable cash. Calculate it by counting the number of invoices customers pay for over a time period, then use that to divide the total number of days it takes each of those customers to pay their invoices. Increase this number by investing in FSM software that allows techs to create paperless invoices and collect payments right at a job site, and that can send automatic reminders to customers who haven’t paid their invoices yet.
5. Customer Retention Rate
This is the rate at which your customers come back to you for repeat business. To calculate it, pick a time period to measure. Then take the number of customers you had at the end of the time period and subtract the number of new customers you gained over the same time period. Then divide the result by the number of customers you had at the beginning of the time period. Then multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage. A low rate may indicate missed upsell and cross-sell opportunities because customers hire you for single specific jobs. Or your problem could be poor work quality or customer service (or both).
Deep Dive
There are many more important metrics besides these ones. We have a list of 40 of them in our article on defining and tracking critical field service metrics and KPIs.
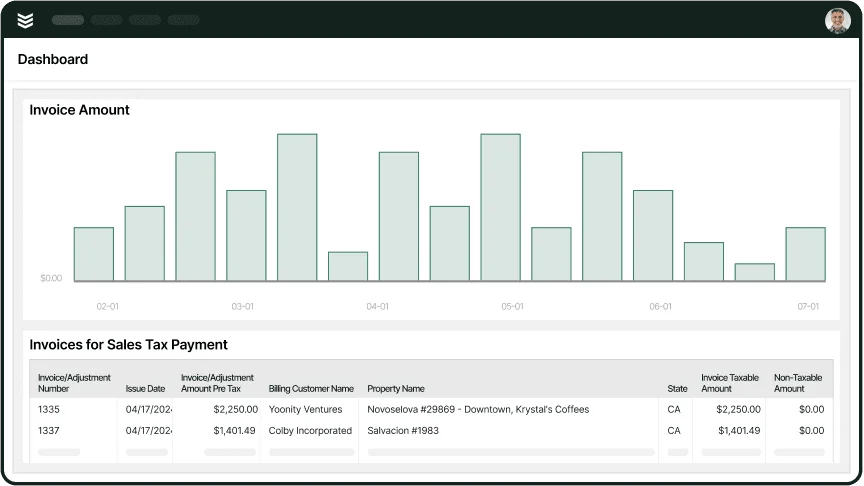
7 key field service dashboards to set up to measure ops success
Setting up various dashboard views in FSM software makes it easy to see at a glance how effectively different parts of your field service operations are working. It can also simplify adjusting certain processes on the fly based on your metrics, or even automating some tasks. Here are 7 areas of FSM we recommend monitoring and controlling with dashboards.
- Invoicing & Payments – Measure the amount invoices are for to catch pricing errors and track your revenue. Track when invoices are sent out and when they’re paid to send automated reminders to overdue customers.
- Scheduling & Dispatch – See when service calls are scheduled, which jobs your techs are qualified to do, and when your techs are available to spread out your workload and prevent burnout.
- Resource & Inventory Management – Track the number and condition of parts and tools you have so you know what’s available for jobs. Automatically order new inventory when your parts stock gets low or tools get worn out.
- Fleet Management – Measure vehicle fuel, mileage, and use to optimize service routes and vehicle workloads, reducing fuel and maintenance costs.
- Technician Productivity – Measure metrics like response time, job completion time, first-time fix rate, and total jobs completed to see how much each of your techs is contributing to your company’s revenue.
- Customer Satisfaction – Respond promptly to customer requests, questions, and feedback. Measure customer ratings of your company’s attributes, customers’ likelihood to refer someone, and customer gain & loss to see how satisfied customers are with your service speed, quality, and friendliness.
- Financial Analytics – Track service call costs and revenue to catch billing errors, adjust your prices, and look for opportunities to upsell or cross-sell.
Deep Dive
For more on field service dashboards, including advice on how to set them up, check out our article on field service dashboards, where we cover which ones to use and how to set them up.
4 types of field service report templates
Field service data is easier to analyze if it’s neatly organized. That’s why it’s handy to have templates to allow your field techs to enter data in a more structured way. This not only makes the data easier to interpret, but it also helps to make sure your techs accurately collect complete sets of the data you need in the first place.
There are several places you can get field service report templates, including:
1. Field service reporting software with built-in templates
Some field service management programs have templates for reports baked right into the software. These templates often conveniently sync with other parts of the software where the data needs to go, reducing the need to enter data multiple times and so limiting the risk of errors. Some templates can even be customized based on your company’s needs while still sending data to the functions that need it. It’s all digital too, so you don’t need to deal with physical paperwork when keeping records.
2. Free downloadable templates
If you don’t have field service management software, or the platform you use doesn’t have the kind of templates you need, you can find free templates scattered online. They’re a simple way to add structure to your field report data, but require more manual data entry and so are more prone to human error. For digital templates, you may have to copy the template every time you make a report, leading to scattered report files that are difficult to tell apart unless you name and organize them carefully. You may even have to print some templates to use them, which leads to inefficient manual paperwork filing.
3. Spreadsheet & document templates
These are templates created using common office software including word processors like Microsoft Word and Google Docs or spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets. Many employees are already at least somewhat familiar with these apps, allowing for quick data entry and customization. Like with other downloadable templates, though, they often require more manual data entry and making file copies of the template to create new reports. This can lead to mistakes and inefficiencies in data entry and filing. Finally, you may have to pay to access some of them.
4. Online template libraries
These have numerous different types of templates, and may include ones tailored to specific trades. Again, though, some require payment to access. And like other types of templates not integrated into field service management software, they require greater manual input and having to copy template files to write new reports. This is inefficient and can lead to human error in writing and organizing your reports.
Deep Dive
For some samples of field reporting templates we like, read our article on the top 12 field service report templates.
If you’re looking specifically for field service templates made for Microsoft Excel, our article on the 10 best Excel field service report templates has some examples. It also shares some pros and cons you should keep in mind for using Excel to write field service reports.
Our guide to writing and using field service reports has more information about the whole process of reporting on field service work. It covers what a report is, what it should include, and how to write one effectively. It also explains things like how to automate some reporting steps with field management software, and how that can save you time and money compared to writing and filing physical reports. To see a practical example of that, have a look at our construction analytics and reporting software!
Top 5 field service management software tools for contractors
So which software programs are the best at field service management? That depends on your industry, the general kinds of work you take on, and several other things. To show you what we mean, here’s a list of the top 5 field management platforms for different field work situations.
1. Best for commercial: BuildOps
BuildOps is designed specifically to help contractors keep field ops in commercial projects under control. Features like advanced search with customer asset hierarchies, a mobile app with AI capabilities, and a real-time dispatch board help find customer and property information, write reports, send invoices, and quickly assign techs to new tasks. All that helps you keep your overall project running smoothly.
Industry Specializations: HVAC, refrigeration, electrical, plumbing, fire safety
How Pricing Works: Per-month-per-user cost
What Sets It Apart: Customer asset management hierarchies that make it easy to see information on all properties a customer owns
Take a closer look at BuildOps
Optimize your field service operations so your teams stay aligned on all jobs.
2. Best for residential: mHelpDesk
Image Source: mHelpDesk
mHelpDesk is known for its ease of use (including its mobile app) and reliable essential field service management functions. Its customer self-serve portal also makes it easy for customers to get help and updates or pay bills. Its automation, reporting, and analytics capabilities aren’t so good, though. It also doesn’t scale well for larger teams working on complicated commercial projects.
Industry Specializations: HVAC, electrical, plumbing, landscaping, security, home cleaning + 22 others
How Pricing Works: Contact them for a quote
What Sets It Apart: Strong core field service management capabilities at an affordable price
3. Best for general contractors: Tradify
Image Source: Tradify
While it contains core FSM capabilities, Tradify has some particular characteristics that make it an especially good general contractor field service management solution. It’s an access-from anywhere cloud platform that allows for booking service calls through its mobile app and syncing your team’s schedules through Google Calendar. These features are very useful for contractors who have to manage multiple projects at the same time. However, Tradify’s functions are pretty limited unless you get at least a Pro-tier subscription.
Industry Specializations: HVAC, plumbing, electrical, gas, refrigeration + 20 others
How Pricing Works: $47-$61/user/month
What Sets It Apart: General contractor can control subcontractors’ schedules from a master calendar (only with Pro plan or better)
4. Best for construction: Buildertrend
Image Source: Buildertrend
Buildertrend is what you’d call construction project management software. In place of typical field service management functions, it has high-level project management features to manage things like sales, job costing, inventory, CRM, and general finances. It’s designed with home builders and remodelers in mind, so it’s not as well suited for large and complicated commercial building construction.
Industry Specializations: Home builders, home remodelers, and general/specialty contractors
How Pricing Works: May be based on contractor type and revenue; contact them for a quote
What Sets It Apart: Ideal for contractors who oversee several long-term or complicated construction projects in a year
5. Best for speciality contractors & designers: Procore
Image Source: Procore
Procore, like Buildertrend, focuses on high-level construction project management. This includes contract bidding, building modeling, financial and resource management, and process efficiency optimizing using analytics and AI-driven workflows. The trade-off is it doesn’t have many functions for managing on-the-ground fieldwork. So contractors looking to manage daily field operations might find Procore has a lot of what they don’t need and not enough of what they do need.
Industry Specializations: HVAC, plumbing, electrical, concrete, structural engineering, construction site preparation, interior & exterior finishing
How Pricing Works: May be based on industry niche, revenue, and products wanted; contact them for a quote
What Sets It Apart: Best high-level project management software for general contractor and specialty contractors
We have even more options for you to choose from – 20 in all – in our list of the best field service management software. If you’re wanting more mobile-first field service software, read our list of the 10 best field service apps, or get an overview of what BuildOps’ own field service mobile app can do for your techs.
Expert Tip
If you’re stuck on deciding between your options – or just need a little more help getting started – our Field Service Management Software Pricing Comparison Guide is here to assist. It tells you what you can expect to pay for field management software, what affects its price most, how to effectively shop for it, and how to get the most value for your money out of the solution you choose. It even has a checklist of things to ask in a demo.
We designed BuildOps with the features commercial contractors need to handle complicated, multi-phase, and multi-property projects. Customer hierarchies let you see which properties a customer owns and if you have to contact a different person for each one. Advanced search that’s able to guess at what you’re looking for instead of needing to match it exactly. A real-time dispatch board that lets dispatchers easily fill time gaps and lets techs know where they need to be, when they need to be there. BuildOps has all of these features as standard. Many of our competitors don’t.
Curious to see BuildOps in action?
Keep teams aligned on the jobsite so you can stay organized and boost profits.










